Human Cytomegalovirus
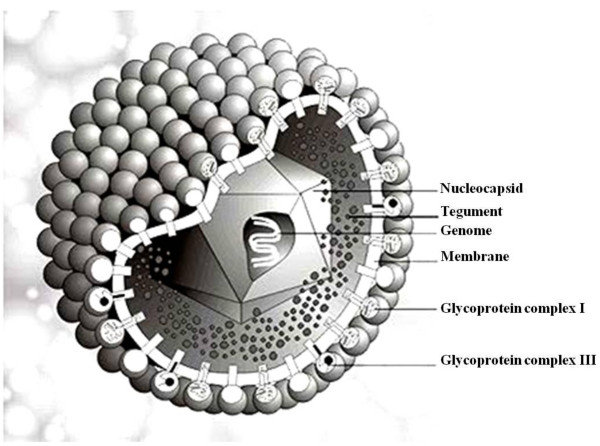
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), also referred to in recent literature as human herpes virus 5 (HHV-5), belongs to the Herpesviridae family, subfamily Betaherpesviridae, genus Cytomegalovirus. It was isolated in 1956 for the first time. The name is derived from the fact that it causes enlargement of the infected cell (cytomegaly) and induces characteristic inclusion bodies. In the blood, it is predominantly cell-associated, above all with granulocytes and macrophages. The HCMV genome consists of a double-stranded DNA with approximately 230,000 bp. The genome is enclosed by an icosahedral capsid (100–110 nm diameter, 162 capsomers). Between the capsid and the virus envelope is a protein layer known as the tegument. The virus envelope is derived from cell membranes. At least eight different viral glycoproteins are embedded in the lipid bilayer. The mature viral particle has a diameter of 150–200 nm. Like all herpesviruses, HCMV is sensitive to low pH, lipid-dissolving agents, and heat. HCMV has a half-life of approximately 60 min at 37 °C and is relatively unstable at −20 °C. It needs to be stored at at least −70 °C in order to maintain its infectivity.
Envelope glycoprotein B (P06473 )
Function
Envelope glycoprotein that plays a role in host cell entry, cell to-cell virus transmission, and fusion of infected cells. May be involved in the initial attachment via binding to heparan sulfate together with the gM/gN complex that binds heparin with higher affinity. Interacts with host integrin ITGB1, PDGFRA and EGFR that likely serve as postattachment entry receptors. Participates also in the fusion of viral and cellular membranes leading to virus entry into the host cell. Membrane fusion is mediated by the fusion machinery composed at least of gB and the heterodimer gH/gL.
G-protein coupled receptor homolog US28 (P69332 )
Function
Receptor for a C-C type chemokine. Binds to a number of different CC-chemokines including CCL5/RANTES, CCL2/MCP-1, CCL3/MIP-1-alpha as well as CX3CL1/Fractalkine. Transduces signals resulting in the activation of MAP kinase signaling pathways and augmentation of intracellular calcium ion levels, leading to alterations in chemotactic behavior of vascular smooth muscle cells and macrophages. The US28 receptor also exhibits high levels of agonist-independent signaling activity and agonist-independent endocytosis. Interacts with endogenous Gaq/11 subunits and thereby constitutively activates phospholipase C.
65 kDa phosphoprotein (P06725 )
Function
Counteracts the host antiviral immune response when activated and phosphorylated, by preventing host IRF3 from entering the nucleus (PubMed:15452220).
Inhibits also the type I interferon production by inactivating the enzymatic activity of DNA sensor CGAS without affecting STING1 (PubMed:29263269).
Participates in the transactivation of viral major immediate-early genes by the recruitment of host IFI16 to the promoters pf these genes (PubMed:20504932).
Envelope glycoprotein H (P12824)
Function
The heterodimer glycoprotein H-glycoprotein L is required for the fusion of viral and plasma membranes leading to virus entry into the host cell. Following initial binding to host receptor, membrane fusion is mediated by the fusion machinery composed of gB and the heterodimer gH/gL. May also be involved in the fusion between the virion envelope and the outer nuclear membrane during virion morphogenesis (By similarity).
In human cytomegalovirus, forms two distincts complexes to mediate viral entry, a trimer and a pentamer at the surface of the virion envelope. The gH-gL-gO trimer is required for infection in fibroblasts by interacting with host PDGFRA. The gH-gL-UL128-UL130-UL131A pentamer is essential for viral entry in epithelial, endothelial and myeloid cells via interaction with host NRP2 (By similarity).
Uncharacterized protein UL130 (P16772)
Function
Plays a role in viral entry into host cells. Forms a pentameric complex at the surface of the viral envelope together with gH, gL, UL130 and UL131. This complex is required for entry in epithelial, endothelial and myeloid host cells. Mechanistically, engages host receptor(s) including neurophilin 2/NRP2 to mediate infection.
Uncharacterized protein UL128 (P16837)
Function
Plays a role in viral entry into host cells. Forms a pentameric complex at the surface of the viral envelope together with gH, gL, UL130 and UL131. This complex is required for entry in epithelial, endothelial and myeloid host cells. Mechanistically, engages host receptor(s) including neurophilin 2/NRP2 to mediate infection. Additionally, monomeric UL128 may interfere with certain inflammatory cytokines to increase infection and dissemination by blocking monocytes migration.
Host species: Human
Isotype: IgG1, kappa
Applications: Research Grade Biosimilar
Expression system: Mammalian Cells
Host species: Human
Isotype: IgG1
Applications: ELISA, Neutralization
Accession: P13201
Applications: ELISA, Immunogen, SDS-PAGE, WB, Bioactivity testing in progress
Expression system: E. coli
Accession: AMO64957.1
Protein length: Asp12-Glu382
Applications: ELISA, Immunogen, SDS-PAGE, WB, Bioactivity testing in progress
Expression system: E. coli
Accession: P06725
Protein length: Thr297-Tyr510
Host species: Human
Isotype: IgG1, kappa
Applications: ELISA, Neutralization
Accession: P13201
Host species: Human
Isotype: IgG1, kappa
Applications: ELISA, Neutralization
Accession: P13201
Host species: Alpaca
Isotype: VHH-8His
Applications: ELISA
Expression system: Mammalian Cells
Host species: Human
Isotype: IgG1, kappa
Applications: Neutralization
Accession: P13201
Applications: ELISA, Immunogen, SDS-PAGE, WB, Bioactivity testing in progress
Expression system: Mammalian Cells
Accession: P12824
Protein length: Arg24-Leu720
Host species: Human
Isotype: IgG1
Applications: FCM, Neutralization
Expression system: Mammalian Cells