Catalog No.
KDB95803
Description
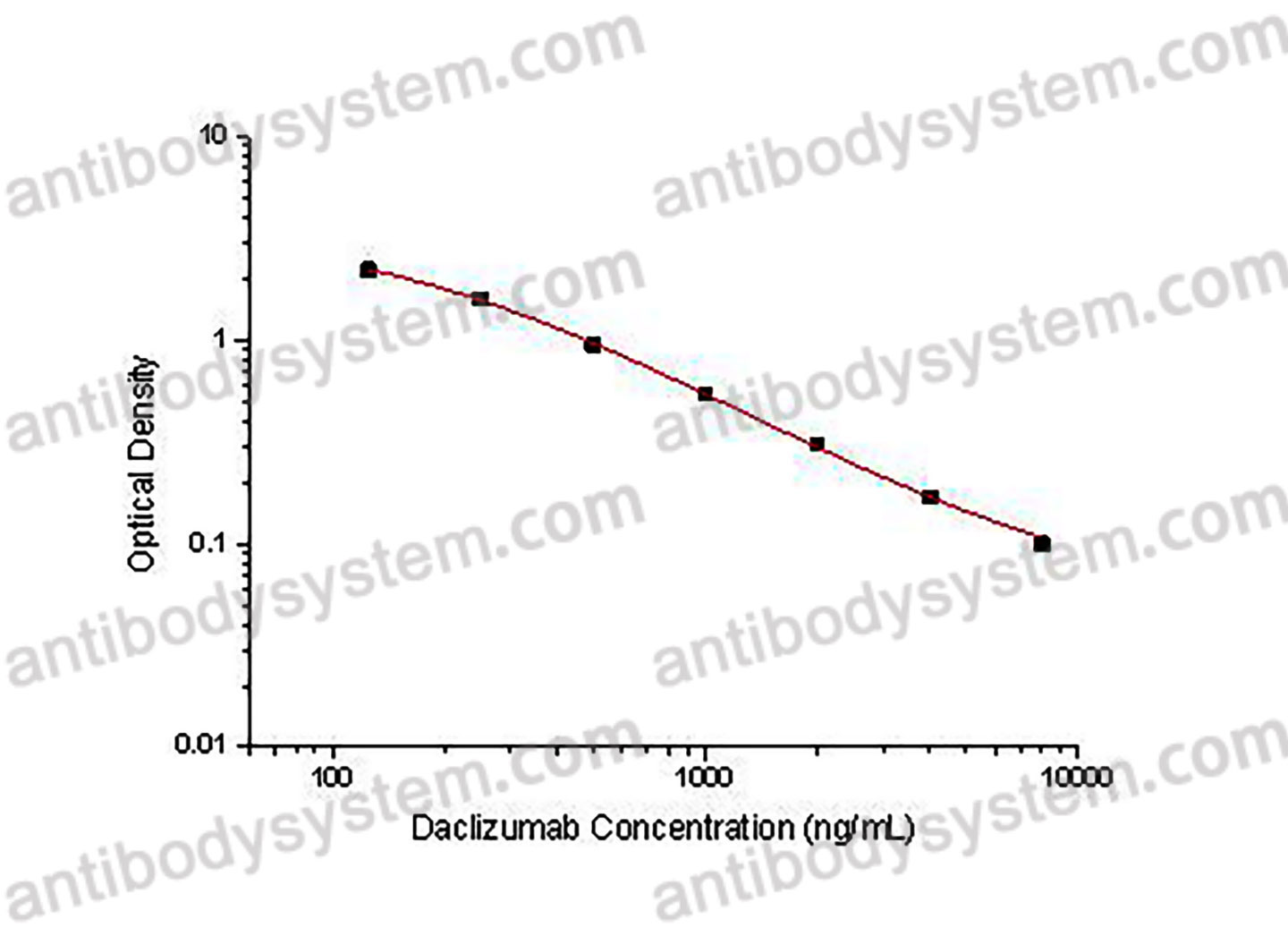
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This assay employs the quantitative competitive enzyme immunoassay technique. Recombinant Human CD25 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards or samples are premixed with biotin-labeled antibody and then pipetted into the wells. Daclizumab in the sample competitively binds to the pre-coated protein with biotin-labeled Daclizumab. After washing away any unbound substances, Streptavidin-HRP is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in inversely proportion to the amount of Daclizumab bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Applications
Used for the quantitative determination of Daclizumab concentration in serum and plasma.
Detection method
Colorimetric
Sample type
Plasma, Serum
Assay type
Quantitative
Range
125 - 8,000 ng/mL
Sensitivity
15.36 ng/mL
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested sixteen times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty four separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
|
|
Intra-Assay Precision
|
Inter-Assay Precision
|
|
Sample
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
n
|
16
|
16
|
16
|
24
|
24
|
24
|
|
Mean (ng/mL)
|
3628.6
|
1096.4
|
247.6
|
5413.0
|
1458.1
|
198.3
|
|
Standard deviation
|
162.1
|
117.1
|
44.8
|
897.3
|
260.3
|
40.0
|
|
CV (%)
|
4.5
|
10.7
|
18.1
|
16.6
|
17.9
|
20.2
|
Recovery
80-120%
Shipping
2-8 ℃
Stability and Storage
When the kit was stored at the recommended temperature for 6 months, the signal intensity decreased by less than 20%.
Alternative Names
BIIB019, DAC HYP, CAS: 152923-56-3
Background
Daclizumab (DAC) is a humanized, monoclonal antibody that blocks CD25, a critical element of the high-affinity interleukin-2 receptor (IL-2R). DAC HYP blockade of CD25 inhibits effector T cell activation, regulatory T cell expansion and survival, and activation-induced T-cell apoptosis. Because CD25 blockade reduces IL-2 consumption by effector T cells, it increases IL-2 bioavailability allowing for greater interaction with the intermediate-affinity IL-2R, and therefore drives the expansion of CD56bright natural killer (NK) cells. Furthermore, there appears to be a direct correlation between CD56bright NK cell expansion and DAC HYP efficacy in reducing relapses and MRI evidence of disease activity in patients with RMS in phase II and phase III double-blind, placebo- and active comparator-controlled trials. Therapeutic efficacy was maintained during open-label extension studies. However, treatment was associated with an increased risk of rare adverse events, including cutaneous inflammation, autoimmune hepatitis, central nervous system Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) syndrome, and autoimmune Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) alpha immunoglobulin-associated encephalitis. As a result, DAC HYP was removed from clinical use in 2018. The lingering importance of DAC is that its use led to a deeper understanding of the underappreciated role of innate immunity in the potential treatment of autoimmune disease.
Induction With Antithymocyte Globulin Is Associated With Decreased Mortality and PTLD in Pediatric Liver Transplantation: A UNOS Data Analysis., PMID:40490923
A peek into the pipeline: Expert views on emerging therapies., PMID:40239631
T-bet+ CXCR3+ B cells drive hyperreactive B-T cell interactions in multiple sclerosis., PMID:40107244
Evolving Patterns of Initial RRMS Treatment in Finland (2013-2022): Insights From a Nationwide Multiple Sclerosis Register., PMID:39935206
Autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for treatment of multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder - recommendations from ECTRIMS and the EBMT., PMID:39814869
Identifying Promising Immunomodulators for Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) and Islet Transplantation., PMID:39735417
Intrathecal immune reactivity against Measles-, Rubella-, and Varicella Zoster viruses is associated with cerebrospinal fluid inflammation in multiple sclerosis., PMID:39377663
Immunomodulators and immunosuppressants for progressive multiple sclerosis: a network meta-analysis., PMID:39254048
Autoantigen-specific CD4+ T cells acquire an exhausted phenotype and persist in human antigen-specific autoimmune diseases., PMID:39226901
Exploration of the Shared Gene Signatures and Molecular Mechanisms between Chronic Bronchitis and Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-associated Glomerulonephritis: Evidence from Transcriptome Data., PMID:38847168
Alterations of Thymus-Derived Tregs in Multiple Sclerosis., PMID:38838284
Induction therapy in heart transplantation: A systematic review and network meta-analysis for developing evidence-based recommendations., PMID:38716786
Interleukin inhibitors and the associated risk of candidiasis., PMID:38605952
Disease-modifying therapies in managing disability worsening in paediatric-onset multiple sclerosis: a longitudinal analysis of global and national registries., PMID:38547883
The Effect of Induction Therapy on Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplantation: A Network Meta-Analysis Using Recent Data., PMID:38490831
Drug-Induced Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis., PMID:38321317
Non-IL-2-blocking anti-CD25 antibody inhibits tumor growth by depleting Tregs and has synergistic effects with anti-CTLA-4 therapy., PMID:38180065
Immunomodulators and immunosuppressants for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a network meta-analysis., PMID:38174776
Outcomes of kidney transplantation in patients with IgA nephropathy based on induction: A UNOS data analysis., PMID:38127110
Adverse effects of immunotherapies for multiple sclerosis: a network meta-analysis., PMID:38032059
Network meta-analysis on efficacy and safety of different biologics for ulcerative colitis., PMID:37803294
"No association between disease modifying treatment and fatigue in multiple sclerosis"., PMID:37708819
A genome-wide association study of blood cell morphology identifies cellular proteins implicated in disease aetiology., PMID:37596262
A Real-World Disproportionality Analysis of Drug-Induced Immune Hemolytic Anemia in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System., PMID:37522435
Treatment with Biologic Drugs in Pediatric Behçet's Disease: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Published Data., PMID:37382804
Microbial peptides activate tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in glioblastoma., PMID:37198490
A first case of successful using of ibrutinib in treating paraneoplastic pemphigus related bronchiolitis obliterans concurrent with CLL., PMID:37007770
Seizure risk in multiple sclerosis patients treated with disease-modifying therapy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis., PMID:36802988
Dynamics of Inflammatory and Neurodegenerative Biomarkers after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Multiple Sclerosis., PMID:36142860
What Have Failed, Interrupted, and Withdrawn Antibody Therapies in Multiple Sclerosis Taught Us?, PMID:35794296
Novel multiple sclerosis agents-associated cardiotoxicity: A real-world pharmacovigilance study., PMID:35643216
Long-term efficacy and safety of siponimod in patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: Analysis of EXPAND core and extension data up to >5 years., PMID:35380078
The Shared Mechanism and Candidate Drugs of Multiple Sclerosis and Sjögren's Syndrome Analyzed by Bioinformatics Based on GWAS and Transcriptome Data., PMID:35356004
Decreased Intrathecal Concentrations of Free Light Chains Kappa in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Taking Very High Effective Disease-Modifying Treatment., PMID:35328273
Current Knowledge of Biologics in Treatment of Noninfectious Uveitis., PMID:35133890
Trends in the use of disease-modifying therapies among reproductive-aged women with multiple sclerosis in the United States from 2010 to 2019., PMID:35088492
Mechanistic and Biomarker Studies to Demonstrate Immune Tolerance in Multiple Sclerosis., PMID:35069562
NK Cells and Innate-Like T Cells After Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Multiple Sclerosis., PMID:34975899
Antibody-guided design and identification of CD25-binding small antibody mimetics using mammalian cell surface display., PMID:34764369
Meta-Analysis of Interleukin-2 Receptor Antagonists as the Treatment for Steroid-Refractory Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease., PMID:34621279
Biologic Therapies and Small Molecules for the Management of Non-Infectious Scleritis: A Narrative Review., PMID:34476773
Correction: Bortezomib for anti-NMDAR encephalitis following daclizumab treatment in a patient with multiple sclerosis., PMID:34396130
Maintenance treatment with infliximab for ulcerative ileitis after intestinal transplantation: A case report., PMID:34307578
Bortezomib for anti-NMDAR encephalitis following daclizumab treatment in a patient with multiple sclerosis., PMID:34079936
Impact of Interferons and Biological Drug Inhibitors of IL-2 and IL-6 on Small-Molecule Drug Metabolism Through the Cytochrome P450 System., PMID:34078115
A Network Meta-Analysis of Induction Immunosuppression for Simultaneous Pancreas-Kidney Transplant From Randomized Clinical Trials., PMID:34053419
Multiple sclerosis: doubling down on MHC., PMID:34006391