Catalog No.
RVV15104
Species reactivity
Epstein-Barr virus (strain B95-8) (HHV-4) (Human herpesvirus 4), Epstein-Barr virus (strain GD1) (HHV-4) (Human herpesvirus 4)
Host species
Human
Isotype
IgG1, kappa
Clonality
Monoclonal
Target
Envelope glycoprotein H, gH, BXLF2
Concentration
1.3 mg/ml
Endotoxin level
Please contact with the lab for this information.
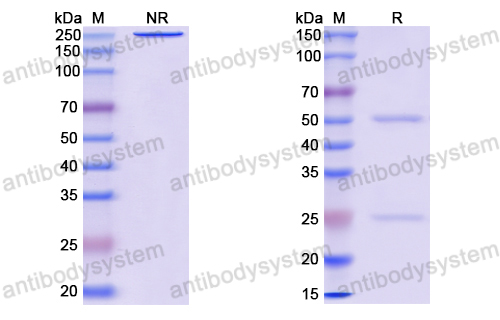
Purity
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Purification
Protein A/G purified from cell culture supernatant.
Accession
P03231, K9US75
Applications
ELISA, FCM, Neutralization, SPR
Form
Liquid
Storage buffer
0.01M PBS, pH 7.4.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Store at 4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Store at -20°C 12 months. Store at -80°C long term.
Clone ID
AMMO1
Neutralizing Antibodies Protect against Oral Transmission of Lymphocryptovirus. PMID: 32724901
Immunization with a self-assembling nanoparticle vaccine displaying EBV gH/gL protects humanized mice against lethal viral challenge. PMID: 35705092
An Antibody Targeting the Fusion Machinery Neutralizes Dual-Tropic Infection and Defines a Site of Vulnerability on Epstein-Barr Virus. PMID: 29669253
gH/gL supercomplexes at early stages of herpesvirus entry. PMID: 26849495
The Human Cytomegalovirus Protein UL116 Interacts with the Viral Endoplasmic-Reticulum-Resident Glycoprotein UL148 and Promotes the Incorporation of gH/gL Complexes into Virions. PMID: 34011552
Non-redundant and redundant roles of cytomegalovirus gH/gL complexes in host organ entry and intra-tissue spread. PMID: 25659098
Structural and biochemical studies of HCMV gH/gL/gO and Pentamer reveal mutually exclusive cell entry complexes. PMID: 25624487
Mutagenesis of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein L Disproportionately Disrupts gH/gL/gO over gH/gL/pUL128-131. PMID: 34132577
Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein gO complexes with gH/gL, promoting interference with viral entry into human fibroblasts but not entry into epithelial cells. PMID: 21880752
Antigenic Characterization of the HCMV gH/gL/gO and Pentamer Cell Entry Complexes Reveals Binding Sites for Potently Neutralizing Human Antibodies. PMID: 26485028
Functional analysis of glycoprotein L (gL) from rhesus lymphocryptovirus in Epstein-Barr virus-mediated cell fusion indicates a direct role of gL in gB-induced membrane fusion. PMID: 19457993
A viral regulator of glycoprotein complexes contributes to human cytomegalovirus cell tropism. PMID: 25831500
Pathogen at the Gates: Human Cytomegalovirus Entry and Cell Tropism. PMID: 30544948
Human Cytomegalovirus gH/gL Forms a Stable Complex with the Fusion Protein gB in Virions. PMID: 27082872
Scanning Mutagenesis of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein gH/gL. PMID: 26656708
Characterization of the human cytomegalovirus gH/gL/UL128-131 complex that mediates entry into epithelial and endothelial cells. PMID: 17942555
Expression Levels of Glycoprotein O (gO) Vary between Strains of Human Cytomegalovirus, Influencing the Assembly of gH/gL Complexes and Virion Infectivity. PMID: 29743375
Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein complex gH/gL/gO uses PDGFR-α as a key for entry. PMID: 28403202
Entry of betaherpesviruses. PMID: 31439151
Soluble Epstein-Barr virus glycoproteins gH, gL, and gp42 form a 1:1:1 stable complex that acts like soluble gp42 in B-cell fusion but not in epithelial cell fusion. PMID: 16973550
Human cytomegalovirus gH/gL/UL128/UL130/UL131A complex elicits potently neutralizing antibodies in mice. PMID: 24837507
Principles for studying in vivo attenuation of virus mutants: defining the role of the cytomegalovirus gH/gL/gO complex as a paradigm. PMID: 25782576
Herpes simplex virus gD forms distinct complexes with fusion executors gB and gH/gL in part through the C-terminal profusion domain. PMID: 19386594
Epstein-Barr virus uses different complexes of glycoproteins gH and gL to infect B lymphocytes and epithelial cells. PMID: 9621012
The Human Cytomegalovirus UL116 Gene Encodes an Envelope Glycoprotein Forming a Complex with gH Independently from gL. PMID: 26937030
Human Cytomegalovirus gH/gL/gO Promotes the Fusion Step of Entry into All Cell Types, whereas gH/gL/UL128-131 Broadens Virus Tropism through a Distinct Mechanism. PMID: 26085146
Formation and characteristics of alginate and anthocyanin complexes. PMID: 32698067
A Viral Pilot for HCMV Navigation? PMID: 26184287
Role of fibronectin on the clearance and tissue uptake of antigen and immune complexes in rats. PMID: 3316274
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Entry Glycoproteins Form Complexes before and during Membrane Fusion. PMID: 35972147
Expression and reconstitution of the gH/gL/gO complex of human cytomegalovirus. PMID: 12361760
Guinea pig cytomegalovirus trimer complex gH/gL/gO uses PDGFRA as universal receptor for cell fusion and entry. PMID: 32791352
Protein-polysaccharide complexes as surfactants. PMID: 3748120
Eph Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Are Functional Entry Receptors for Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68., PMID:40501621
High IgG titers against EBV glycoprotein 42 correlate with lower risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma., PMID:39959976
Association Between Antibodies That Bind Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) gp350 and gH/gL and Shedding of EBV in Saliva From Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Multiplex Family Members in Taiwan., PMID:39229285
A gH/gL-encoding replicon vaccine elicits neutralizing antibodies that protect humanized mice against EBV challenge., PMID:38926438
Vaccination with nanoparticles displaying gH/gL from Epstein-Barr virus elicits limited cross-protection against rhesus lymphocryptovirus., PMID:38781964
Epstein-Barr virus gp42 antibodies reveal sites of vulnerability for receptor binding and fusion to B cells., PMID:38479361
Urgency and necessity of Epstein-Barr virus prophylactic vaccines., PMID:36494369
Epstein-Barr virus gH/gL has multiple sites of vulnerability for virus neutralization and fusion inhibition., PMID:36306784
Immunization with a self-assembling nanoparticle vaccine displaying EBV gH/gL protects humanized mice against lethal viral challenge., PMID:35705092
Antibody Generation and Immunogenicity Analysis of EBV gp42 N-Terminal Region., PMID:34960650
Immunization with Components of the Viral Fusion Apparatus Elicits Antibodies That Neutralize Epstein-Barr Virus in B Cells and Epithelial Cells., PMID:30979688
An Antibody Targeting the Fusion Machinery Neutralizes Dual-Tropic Infection and Defines a Site of Vulnerability on Epstein-Barr Virus., PMID:29669253
Inhibition of EBV-mediated membrane fusion by anti-gHgL antibodies., PMID:28939750
Structural basis for potent antibody-mediated neutralization of human cytomegalovirus., PMID:28783665
Scanning Mutagenesis of Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein gH/gL., PMID:26656708
Human Cytomegalovirus gH/gL/gO Promotes the Fusion Step of Entry into All Cell Types, whereas gH/gL/UL128-131 Broadens Virus Tropism through a Distinct Mechanism., PMID:26085146
Fusion of Epstein-Barr virus with epithelial cells can be triggered by αvβ5 in addition to αvβ6 and αvβ8, and integrin binding triggers a conformational change in glycoproteins gHgL., PMID:21957301
Structure of a core fragment of glycoprotein H from pseudorabies virus in complex with antibody., PMID:21149698
Point mutations in EBV gH that abrogate or differentially affect B cell and epithelial cell fusion., PMID:17307213
Cell-surface expression of a mutated Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein B allows fusion independent of other viral proteins., PMID:15583133
Epstein-Barr virus gH is essential for penetration of B cells but also plays a role in attachment of virus to epithelial cells., PMID:10864642
Epstein-Barr virus lacking glycoprotein gp42 can bind to B cells but is not able to infect., PMID:9420211
Epstein-Barr virus uses HLA class II as a cofactor for infection of B lymphocytes., PMID:9151859
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF2 gene product associates with the gH and gL homologs of EBV and carries an epitope critical to infection of B cells but not of epithelial cells., PMID:7539502