Catalog No.
KDJ41001
Description
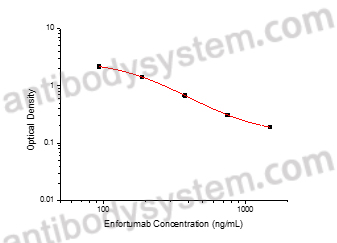
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This assay employs the quantitative competitive enzyme immunoassay technique. Recombinant Human NECTIN4 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards or samples are premixed with biotin-labeled antibody and then pipetted into the wells. Enfortumab in the sample competitively binds to the pre-coated protein with biotin-labeled Enfortumab. After washing away any unbound substances, Streptavidin-HRP is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in inversely proportion to the amount of Enfortumab bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Applications
Used for the quantitative determination of Enfortumab concentration in serum and plasma.
Detection method
Colorimetric
Sample type
Plasma, Serum
Assay type
Quantitative
Range
93.75 - 1,500 ng/mL
Sensitivity
47.39 ng/mL
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested sixteen times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty four separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
|
|
Intra-Assay Precision
|
Inter-Assay Precision
|
|
Sample
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
n
|
16
|
16
|
16
|
24
|
24
|
24
|
|
Mean (ng/mL)
|
692.6
|
160.3
|
91.4
|
652.4
|
163.6
|
95.8
|
|
Standard deviation
|
47.1
|
12.0
|
14.9
|
80.2
|
27.9
|
18.1
|
|
CV (%)
|
6.8
|
7.5
|
16.3
|
12.3
|
17.0
|
18.9
|
Recovery
80-120%
Shipping
2-8 ℃
Stability and Storage
When the kit was stored at the recommended temperature for 6 months, the signal intensity decreased by less than 20%. For unopened kits, if you want to prolong the storage time, please store the Standard, Detection A, Detection B and Microplate at - 20℃, the rest reagents should be store at 4℃.
Alternative Names
AGS-22CE, AGS-22M, AGS-22M6E, unconjugated : AGS-22C3 or AGSM6, CAS: 1346452-25-2
Background
Enfortumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) designed for the treatment of cancer expressing Nectin-4. It was developed through two main lines, hybridoma (ASG-22ME) and Chinese hamster ovary (ASG-22CE). Enfortumab refers to the fully humanized (from mouse) monoclonal antibody (mAb) created by scientists at Agensys (part of Astellas) using Amgen’s transgenic system (XenoMouse), it is the first agent to target Nectin-4 that expressed on many solid tumors especially on bladder cancers. Vedotin refers to the payload drug microtubule-disrupting agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) and the linker. The linker technology holding the antibody and the toxin together was provided by and licensed from Seattle Genetics. Preclinical studies showed that enfortumab vedotin effectively binds to target cells, internalizes and induces cell-killing activity. Mouse and patient xenograft models were used to test enfortumab vedotin’s antitumor activity in human breast, bladder, pancreatic and lung cancers. In March 2018, Seattle Genetics and Astellas received the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Breakthrough Therapy Designation for enfortumab vedotin based on interim results from the phase 1 study examining enfortumab vedotin as monotherapy treatment for patients with metastatic urothelial cancer who were previously treated with checkpoint inhibitors.
Avelumab maintenance in advanced urothelial carcinoma: real-world data from Northern Spain (AVEBLADDER study)., PMID:40514610
Mechanistic Insights into Anti-Nectin4-VcMMAE-Induced Ocular Toxicity: From Cellular Uptake Pathways to Molecular Modification., PMID:40507807
Enfortumab vedotin induced interstitial lung disease: A first case report with pathological evidence from transbronchial lung cryobiopsy., PMID:40496844
Enfortumab Vedotin-Induced Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Acute Tubulointerstitial Nephritis Requiring Intensive Care in the Treatment of Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma: A Case Report., PMID:40487556
Real-world clinical outcomes of sacituzumab govitecan after prior exposure to enfortumab vedotin in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma., PMID:40479863
Two Cases of Enfortumab Vedotin-Induced Drug Eruption Diagnosed Based on the Distinctive Epidermal Mitotic Figures in Patients Receiving Combination Therapy With Pembrolizumab., PMID:40476598
Nectin-4-Targeting Radiotracers: Novel Theranostic Agents for Precision Oncology in Cancer., PMID:40474033
Enfortumab Vedotin Plus Pembrolizumab in Untreated Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: 2.5-Year Median Follow-Up of the Phase III EV-302/KEYNOTE-A39 Trial., PMID:40460988
Adverse cardiac events associated with antibody drug conjugates in cancer patients: a retrospective analysis on the FAERS database and randomized controlled trials., PMID:40455883
Enfortumab vedotin plus pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer (EV-302): patient-reported outcomes from an open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 study., PMID:40449498
Antibody-drug conjugates as game changers in bladder cancer: current progress and future directions., PMID:40433388
Consolidative Surgery for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma Following Induction Enfortumab Vedotin and/or Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: A Multicenter Analysis., PMID:40425390
Mechanistic Insights and Future Directions for Enfortumab Vedotin in Urothelial Carcinoma: Highlights from the 10th Annual Leo & Anne Albert Institute for Bladder Cancer Care and Research Symposium., PMID:40422537
E-VIRTUE: a study of enfortumab vedotin with or without pembrolizumab in rare genitourinary tumors-design and rationale., PMID:40421891
Erythema multiforme-like eruption with severe epidermal necrosis after administration of enfortumab vedotin., PMID:40417899
A Case of Generalized Anhidrosis That Developed During Treatment With Enfortumab Vedotin., PMID:40401791
Zelenectide pevedotin (BT-8009): a bicyclic peptide toxin conjugate targeting nectin-4 for the treatment of bladder cancer., PMID:40401457
Progress of antibody-drug conjugates in the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma: opportunities and challenges., PMID:40377724
The patients have spoken: how does enfortumab vedotin impact quality of life?, PMID:40376537
Evaluation of Optimal Sequential Treatment Patterns and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma Treated With First-Line Platinum-Based Chemotherapy: A Multicenter Collaborative Study., PMID:40375459
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Urothelial Carcinoma: Current Landscape and Future Directions., PMID:40361519
Increased Risk of Hyperglycemia in Advanced Urothelial Cancer Patients Treated with Enfortumab Vedotin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis., PMID:40358559
Complete Response after Avelumab Maintenance Therapy: Successful Management of Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma., PMID:40352709
Salvage Surgery Following Remarkable Tumor Shrinkage With Enfortumab Vedotin in Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma., PMID:40336728
Novel Molecular Biomarkers to Guide Treatment Decision-making in Metastatic Urothelial Cancer-A Patient Cohort Analysis., PMID:40300922
Advancements in systemic therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review from the beginning to the latest updates., PMID:40296876
Treatment Outcomes After Progression With Enfortumab Vedotin in Patients With Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma., PMID:40295063
Steroid Premedication Impact on Efficacy and Cutaneous Toxicity of Enfortumab Vedotin for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma., PMID:40295014
Cancer-induced Pain Is Associated With Poor Overall Survival of Urothelial Carcinoma Patients Treated With Enfortumab Vedotin., PMID:40295006
Real-World Clinical Outcomes with First-Line Systemic Treatment and Avelumab Maintenance in US Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: The SPEAR Bladder-II Study., PMID:40277744
Evaluation of Nectin-4 and Trop-2: Implications for Patient Outcomes and Therapy in Penile Cancer., PMID:40252843
Association between drug-related cutaneous adverse events and survival outcomes in patients treated with enfortumab vedotin., PMID:40252634
Pembrolizumab after platinum-based chemotherapy for metastatic urothelial cancer: comparison between patients from a Dutch nationwide cohort and KEYNOTE-045., PMID:40250101
Clinical Response to Enfortumab Vedotin and Pembrolizumab in a Patient with Vaginal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report., PMID:40235861
Balancing effectiveness, toxicity, and individualization: enfortumab vedotin in advanced urothelial cancer., PMID:40226067
Strategies to overcome resistance to enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab for patients with urothelial carcinoma: harnessing present knowledge for future advances., PMID:40225697
Cost-Effectiveness of Enfortumab Vedotin and Pembrolizumab for First-Line Metastatic Urothelial Cancer in the United States., PMID:40220863
High-glucose-associated YTHDC1 lactylation reduces the sensitivity of bladder cancer to enfortumab vedotin therapy., PMID:40215164
Nectin-4 expression patterns and therapeutics in oncology., PMID:40209851
[Enfortumab-vedotin in combination with pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for advanced/metastatic urothelial carcinoma]., PMID:40204543
Emerging Paradigms in Genitourinary Cancers: Integrating Molecular Imaging, Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Targeted Therapies, and Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Renal Cell and Urothelial Carcinomas., PMID:40198857
Organ-specific tumor response to enfortumab vedotin in metastatic urothelial carcinoma: a multicenter retrospective study., PMID:40197493
Editorial Comment to "Impact of Skin Adverse Events on Prognosis in Patients With Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma Treated With Enfortumab Vedotin: A Real-World Multicenter Study"., PMID:40195588
Lines of Therapy for Locally Advanced/Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: The New Paradigm., PMID:40184571
Impact of Initial Relative Dose Intensity on Tumor Response and Survival Outcomes in Enfortumab Vedotin Monotherapy for Previously Treated Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma: A Real-world Analysis From a Multicenter Study., PMID:40175211
Oncology: What You May Have Missed in 2024., PMID:40163865
Clinical significance of the dose modification of enfortumab vedotin monotherapy for advanced urothelial carcinoma., PMID:40163660
A case of remarkable response to combined radiation therapy, enfortumab vedotin, and pembrolizumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma., PMID:40160871
Recognition and management of adverse cutaneous reactions in patients on enfortumab vedotin and pembrolizumab in the inpatient setting., PMID:40144398
Treatment of Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Cancer., PMID:40139170