Catalog No.
KDD17202
Description
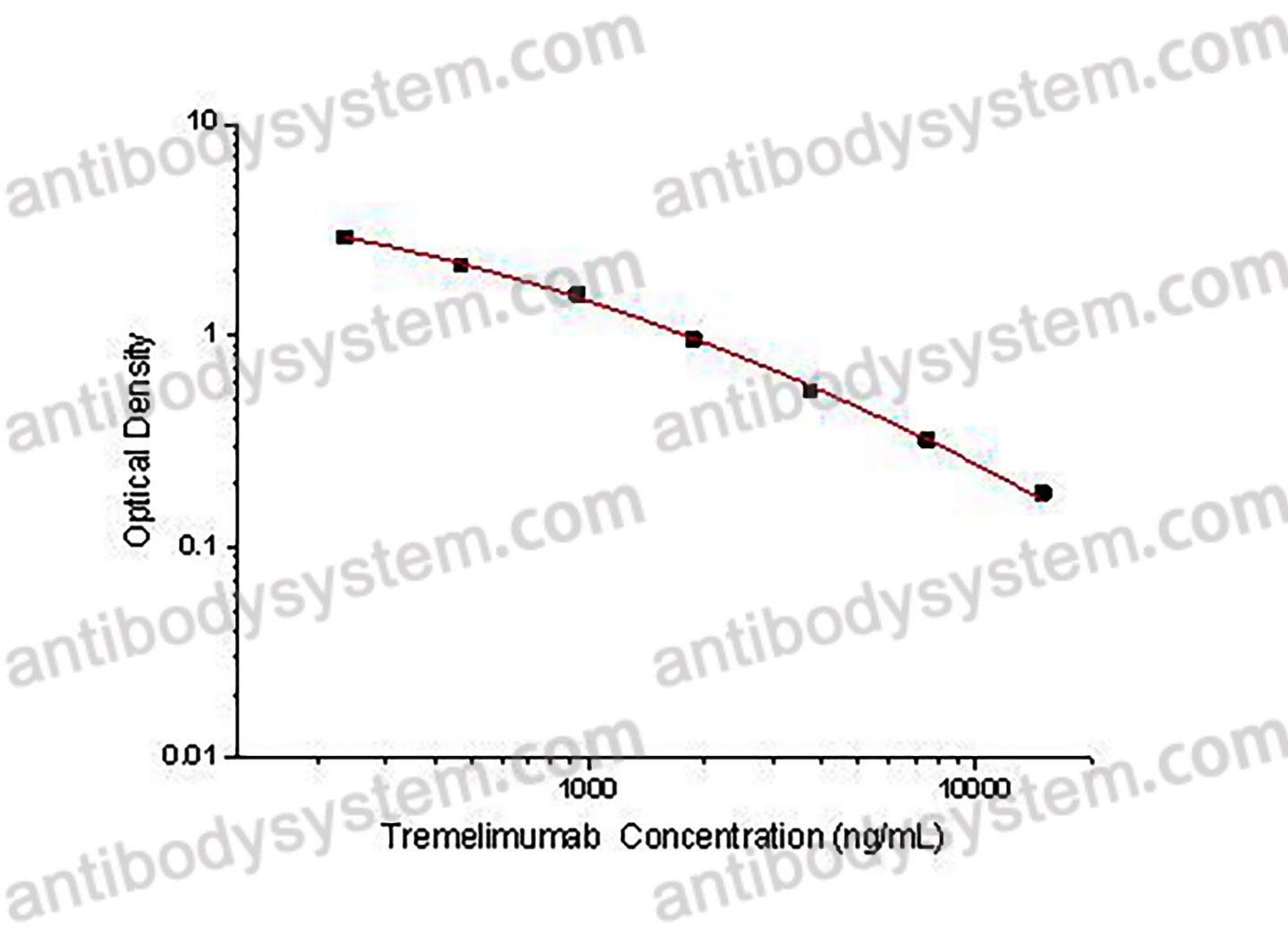
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This assay employs the quantitative competitive enzyme immunoassay technique. Recombinant Human CD152 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards or samples are premixed with biotin-labeled antibody and then pipetted into the wells. Tremelimumab in the sample competitively binds to the pre-coated protein with biotin-labeled Tremelimumab. After washing away any unbound substances, Streptavidin-HRP is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in inversely proportion to the amount of Tremelimumab bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Applications
Used for the quantitative determination of Tremelimumab concentration in serum and plasma.
Detection method
Colorimetric
Sample type
Plasma, Serum
Assay type
Quantitative
Range
234.38 - 15,000 ng/mL
Sensitivity
48.85 ng/mL
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested sixteen times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty four separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
|
|
Intra-Assay Precision
|
Inter-Assay Precision
|
|
Sample
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
n
|
16
|
16
|
16
|
24
|
24
|
24
|
|
Mean (ng/mL)
|
9104.9
|
2196.7
|
423.8
|
9765.7
|
2311.2
|
454.9
|
|
Standard deviation
|
785.0
|
259.7
|
79.9
|
726.8
|
260.2
|
90.0
|
|
CV (%)
|
8.6
|
11.8
|
18.8
|
7.4
|
11.3
|
19.8
|
Recovery
80-120%
Shipping
2-8 ℃
Stability and Storage
When the kit was stored at the recommended temperature for 6 months, the signal intensity decreased by less than 20%.
Alternative Names
Ticilimumab, CP-675, CP-675, 206, CP-675206 clone 11.2.1, CAS: 745013-59-6
Background
Tremelimumab (CP-675,206; previously, ticilimumab) is a fully human IgG2 monoclonal antibody and has a half-life of 22 days, which was generated in a XenoMouse murine system, that has a subnanomolar affinity for binding to human cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) for treatment of patients with advanced cancers. Treatment with an anti-CTLA4 mAb prevents normal downregulation of T cells and prolongs T cell activation, thereby enhancing immune function. Generated at Abgenix (Fremont, CA) using xenomice by Pfizer, Inc. (New York), tremelimumab has been undergoing human trials for the treatment of malignant melanoma. Additionally, tremelimumab is under investigation for the treatment of Mesothelioma, Liver Cancer, Liver Neoplasms, Liver Cell Caricinoma, and HepatoCellular Carcinoma and it has been investigated in Part C: Malignant Mesothelioma and Part A and B: Advanced Solid Malignancies. Recently, it has been announced by AstraZeneca and MedImmune that tremelimumab as monotherapy does not improve survival and the primary end point is not reached (D4880C00003; NCT01843374). Further data regarding DETERMINE was presented at ASCO 2016, detailing that 571 patients were enrolled and that 81% had died throughout the duration of the study. There was no statistically significant difference between treated patients and placebo patients, and side effects such as diarrhoea, loss of appetite and development of rashes were seen at higher rates in treated patients than in placebo treatments. This indicates a need for further research into the use of tremelimumab as a monotherapy as well as use in combination therapy to potentially achieve better clinical outcomes.
Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Overall Survival in Patients With HCC Treated With Durvalumab Plus Tremelimumab., PMID:40515751
Conversion surgery following severe cytokine release syndrome induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors doublet in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma., PMID:40500480
Editorial Comment on "Safety of Partial and Radical Nephrectomy for Complex Locally Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma After Neo-Adjuvant Immune Checkpoint Inhibition - Analysis from a Phase 1b Trial (Durvalumab +/- Tremelimumab)"., PMID:40484289
Immune-mediated enterocolitis is associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A pharmacovigilance study from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database., PMID:40465755
Differential safety profiles of durvalumab monotherapy and durvalumab in combination with tremelimumab in adult patients with advanced cancers., PMID:40447320
Safety of Partial and Radical Nephrectomy for Complex Locally Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma After Neo-Adjuvant Immune Checkpoint Inhibition: Analysis From a Phase 1b Trial (Durvalumab +/- Tremelimumab)., PMID:40441307
A novel approach to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of durvalumab and tremelimumab combination therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma., PMID:40433908
Looking Toward the Future: Emerging Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma., PMID:40416920
Multicenter phase Ib/II study of second-line durvalumab and tremelimumab in combination with paclitaxel in patients with biomarker-selected metastatic gastric cancer., PMID:40399487
Immune-mediated adverse events and overall survival with tremelimumab plus durvalumab and durvalumab monotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: HIMALAYA phase 3 randomized clinical trial., PMID:40384092
First-line durvalumab therapy alone or in combination with tremelimumab for metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A cost-effectiveness analysis., PMID:40378108
Durvalumab with or without tremelimumab in combination with chemotherapy in first-line metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: outcomes by tumor mutational burden in POSEIDON., PMID:40334315
Cost-Utility Analysis of Durvalumab and Tremelimumab Versus Best Supportive Care in Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer., PMID:40320238
Antitumor effects and immune-mediated adverse events of durvalumab plus tremelimumab treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma., PMID:40318087
Peripheral blood CD4+/CD8+ T cell ratio may have potential for predicting the treatment response of durvalumab plus tremelimumab therapy (STRIDE) for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Preliminary report., PMID:40317865
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio at the start of the second course of durvalumab plus tremelimumab therapy predicts therapeutic efficacy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter analysis., PMID:40317623
Evaluating two rechallenge strategies of immune checkpoint inhibitors: Durvalumab plus tremelimumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma., PMID:40317555
Multimodality treatment in synchronous oligometastatic NSCLC: Analysis of the ETOP CHESS trial., PMID:40311307
Tremelimumab plus durvalumab versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a cost-effectiveness analysis from the US payer perspective., PMID:40306910
Pharmacovigilance study on the reporting frequency of atrial fibrillation with immune checkpoint inhibitors: insights from FDA Adverse Event Reporting System., PMID:40290514
Usefulness of the Early Increase of Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte Count in Predicting Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Durvalumab Plus Tremelimumab., PMID:40282450
Prior Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment Is a Risk Factor for Treatment-Related Adverse Events in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated With Durvalumab Plus Tremelimumab., PMID:40276064
A phase I clinical trial of radiation therapy, durvalumab and tremelimumab in recurrent gynecologic cancer., PMID:40273550
Translaminar Screw Fixation for Giant C1 Lateral Mass Metastasis From Hepatocellular Carcinoma., PMID:40271322
Treatment Decision-Making in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Importance of Understanding the Different Response Patterns between IO plus Anti-VEGF and IO plus IO Regimens., PMID:40255877
Cardiological adverse events in hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving immunotherapy: Influence of comorbidities and clinical outcomes., PMID:40245453
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced dyshidrotic eczema following tremelimumab therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma., PMID:40224217
Five-year overall survival update from the HIMALAYA study of tremelimumab plus durvalumab in unresectable HCC., PMID:40222621
Immune check point inhibitors for ocular adnexal and periocular tumors., PMID:40213294
Effects of cannabinoids on immune checkpoint inhibitor response: CCTG pooled analysis of individual patient data., PMID:40184324
A Case of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer With Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Like Features Responding to a Combination of Durvalumab, Tremelimumab, Carboplatin, and Nab-Paclitaxel., PMID:40161114
Mid-term Combination Immunotherapy and its Effect on the Albumin-Bilirubin Score in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma., PMID:40155043
Comparative effectiveness of immunotherapy versus lenvatinib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A real-world analysis using target trial emulation., PMID:40153442
A phase 1 study of durvalumab as monotherapy or combined with tremelimumab with or without azacitidine in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome., PMID:40153010
Fractures Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Disproportionality Analysis of the World Health Organization Pharmacovigilance Database., PMID:40143113
Prompt initiation of durvalumab and tremelimumab for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic active hepatitis B: a phase 2 clinical trial., PMID:40128285
Epigenetic therapy sensitizes anti-PD-1 refractory head and neck cancers to immunotherapy rechallenge., PMID:40091844
Phase 2 study of neoadjuvant durvalumab plus docetaxel, oxaliplatin, and S-1 with surgery and adjuvant durvalumab plus S-1 for resectable locally advanced gastric cancer., PMID:40081945
Mutational Landscape of Recurrent/Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Association with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Outcomes., PMID:40080442
Advances in Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma., PMID:40076561
Treatment outcomes of hepatectomy and systemic chemotherapy based on oncological resectability criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma., PMID:40046525
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy with Dual Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Advanced-Stage Ovarian Cancer: Final Analysis of TRU-D Phase II Nonrandomized Clinical Trial., PMID:40043003
What can real-world data teach us about treating patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma?, PMID:40042586
Higher Absolute Lymphocyte Counts and Lower Des-γ-Carboxyprothrombin Levels After Treatment Initiation Are Associated With the Clinical Efficacy of Tremelimumab Plus Durvalumab Combination Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma., PMID:39989844
Multiomics analysis of immune correlatives in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with tremelimumab plus durvalumab., PMID:39965889
pH-dependent dissociation from CTLA-4 in early endosomes improves both safety and antitumor activity of anti-CTLA-4 antibodies., PMID:39964714
Bladder Preservation with Durvalumab plus Tremelimumab and Concurrent Radiotherapy in Patients with Localized Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (IMMUNOPRESERVE): A Phase II Spanish Oncology GenitoUrinary Group Trial., PMID:39957401
Exacerbation of dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor-associated bullous pemphigoid by the immune checkpoint inhibitors durvalumab and tremelimumab., PMID:39953771
A clinical study of tremelimumab, alone or in combination with olaparib, for recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer., PMID:39951918
Self-Organizing Map-Based Assessment of Immune-Related Adverse Events Caused by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors., PMID:39902026