Catalog No.
KDD12603
Description
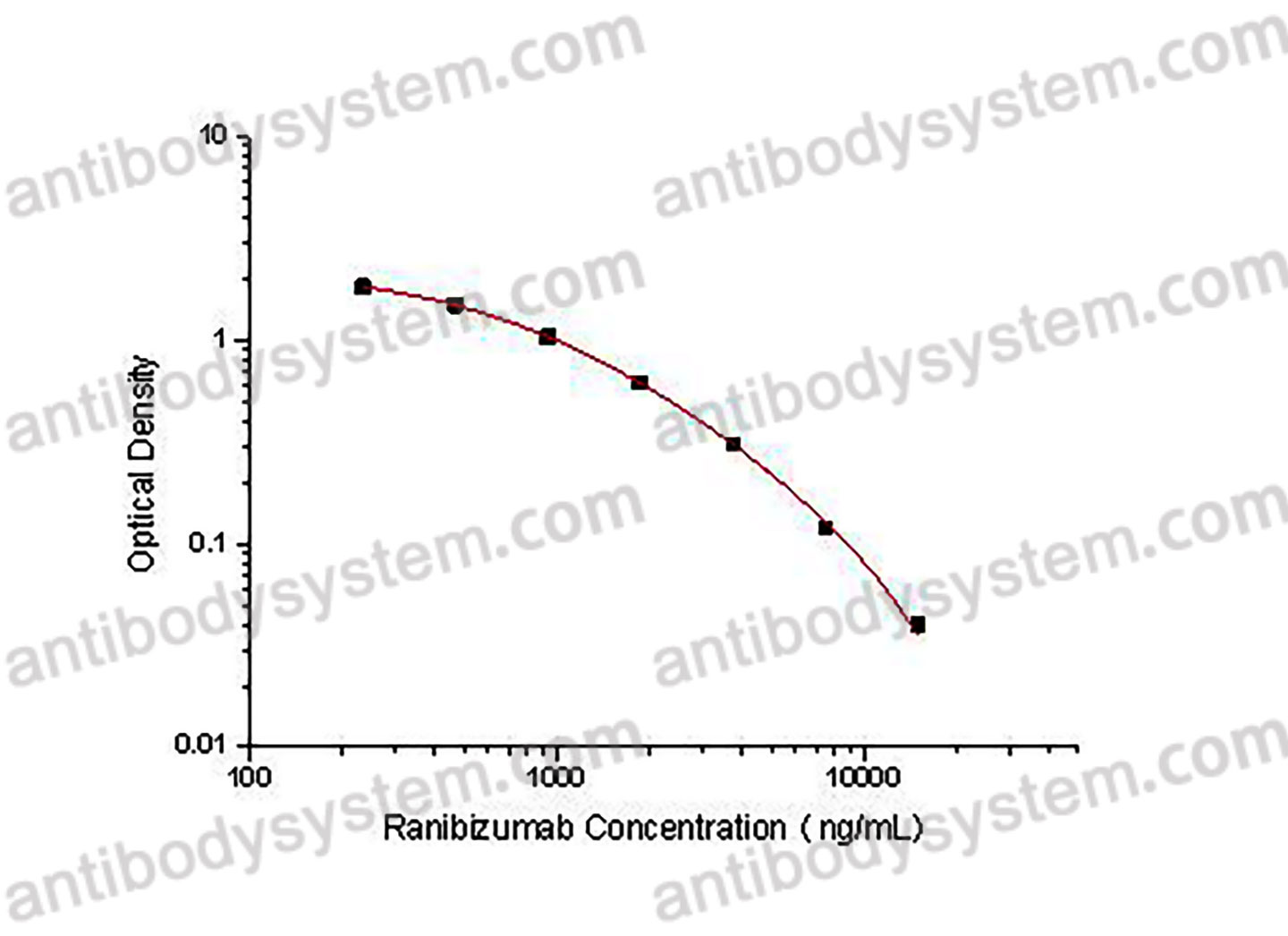
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This assay employs the quantitative competitive enzyme immunoassay technique. Recombinant human VEGFA has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards or samples are premixed with biotin-labeled antibody and then pipetted into the wells. Ranibizumab in the sample competitively binds to the pre-coated protein with biotin-labeled Ranibizumab. After washing away any unbound substances, Streptavidin-HRP is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in inversely proportion to the amount of Ranibizumab bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Applications
Used for the quantitative determination of Ranibizumab concentration in serum and plasma.
Detection method
Colorimetric
Sample type
Plasma, Serum
Assay type
Quantitative
Range
234.4 ng/mL - 15,000 ng/mL
Sensitivity
138.91 ng/mL
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested sixteen times on one plate to assess
intra-assay precision.
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty four separate assays to assess
inter-assay precision.
|
|
Intra-Assay Precision
|
Inter-Assay Precision
|
|
Sample
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
n
|
16
|
16
|
16
|
24
|
24
|
24
|
|
Mean (ng/mL)
|
5082.5
|
957.5
|
530.9
|
5093.9
|
1058.1
|
510.6
|
|
Standard deviation
|
250.3
|
55.5
|
34.0
|
305.7
|
92.4
|
49.9
|
|
CV (%)
|
4.9
|
5.8
|
6.4
|
6.0
|
8.7
|
9.8
|
Recovery
80-120%
Shipping
2-8 ℃
Stability and Storage
When the kit was stored at the recommended temperature for 6 months, the signal intensity decreased by less than 20%.
Alternative Names
Fab-12 variant Y0317, RhuFab, CAS: 347396-82-1
Background
Ranibizumab is a monoclonal antibody fragment (Fab) created from the same parent mouse antibody as bevacizumab. Ranibizumab was developed by Genentech and is marketed in the United States by Genentech and elsewhere by Novartis, under the brand name Lucentis. Ranibizumab is used to treat wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD; an ongoing disease of the eye that causes loss of the ability to see straight ahead and may make it more difficult to read, drive, or perform other daily activities). It is also used to treat macular edema after retinal vein occlusion (an eye disease caused by blockage of blood flow from the eye that leads to blurry vision and vision loss), diabetic macular edema (an eye disease caused by diabetes that can lead to vision loss), and diabetic retinopathy (damage to the eyes caused by diabetes). It inhibits angiogenesis by inhibiting Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), and its effectiveness is similar to that of bevacizumab. Its rates of side effects also appear similar. However, ranibizumab typically costs $2,000 a dose, while the equivalent dose of bevacizumab typically costs $50.
Six-year findings of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in the EVEREST II study: Japanese subgroup analysis., PMID:40504425
Efficacy of switching from existing anti-vascular endothelial growth factor drugs to ranibizumab biosimilar in neovascular age-related macular degeneration., PMID:40500585
Usage of brolucizumab as treatment for wet age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV): A narrative review., PMID:40489855
Effect of ranibizumab on diabetic retinopathy via the vascular endothelial growth factor/STAT3/glial fibrillary acidic protein pathway., PMID:40487605
Response to 'Comment on: 'Comparing safety and efficacy of Bevacizumab, Ranibizumab and Ranibizumab biosimilar in Retinopathy of prematurity"., PMID:40483306
Anti-VEGFs for Diabetic Macular Oedema: Analysis of Efficacy, Safety, and Cost of More Durable Therapies from a Dutch Societal Perspective., PMID:40481910
Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor injections and risks of stroke in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration-A registry-based cohort study., PMID:40481786
Modeling the Ocular Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Ranibizumab for Improved Understanding and Data Collection Strategies in Ocular Diseases., PMID:40478563
EFFICACY AND PROGNOSIS OF ANTI-VEGF AGENTS COMBINED WITH PANRETINAL PHOTOCOAGULATION IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY: A CLINICAL OBSERVATIONAL STUDY., PMID:40466685
Infographic: intravitreal therapy for uveitic macular edema-ranibizumab versus methotrexate versus the dexamethasone implant: the MERIT trial results., PMID:40457097
Association between intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor agents and hypertension: a meta-analysis., PMID:40456283
Anti-VEGF Agents Clearance Through the Aqueous Outflow Pathway in a Rat Model., PMID:40455045
Several Common Genetic Variations Associate With Functional or Anatomic Effects of Anti-VEGF Treatment in Conditions With Macular Edema., PMID:40455044
Targeting VEGF With 99mTc-Labeled Ranibizumab for Noninvasive Diagnosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer., PMID:40444333
Managing Choroidal Neovascularization in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: Outcomes of Vitrectomy and Intravitreal Ranibizumab/Aflibercept Therapy-A Case Report., PMID:40438152
Oral lamivudine in diabetic macular edema: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial., PMID:40436012
Area Under the Curve Analysis in a Real-World Cohort of Finnish Patients Treated for Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration., PMID:40423616
Real-Life Treatment Intervals and Morphological Outcomes Following the Switch to Faricimab Therapy in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration., PMID:40423060
Effectiveness and safety of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapies for macular edema in retinal vein occlusion: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials., PMID:40419166
Subretinal tissue plasminogen activator in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy-related submacular haemorrhage and exudative retinal detachment., PMID:40409770
Efficacy and safety of prophylactic simultaneous intravitreal moxifloxacin injection with standard intravitreal anti-VEGF injection procedure in cases of cystoid macular edema and macular neovascularization., PMID:40405143
Comparison of three loading doses of bevacizumab and ranibizumab for macular edema due to branch retinal vein occlusion., PMID:40405136
[Age-related macular degeneration - Part 2: therapeutic options for AMD]., PMID:40389215
A Study of Visual Outcomes and Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (SD-OCT) Biomarker Changes in Patients Treated With Ranibizumab for Diabetic Macular Edema in a Tertiary Hospital., PMID:40385737
Effect of simultaneous intravitreal ranibizumab and extended-release dexamethasone injection on patients with naïve versus refractory retinal vein occlusion macular edema: a prospective, multicenter, and interventional open-label study., PMID:40385115
Socioeconomic Disparities in Intravitreal Injection Use and Anti-VEGF Agent Selection: Aflibercept/Ranibizumab Versus Bevacizumab., PMID:40383690
Combining ranibizumab with calcium dobesilate to reduce injection frequency in diabetic macular edema treatment., PMID:40381058
Therapeutic outcomes of ranibizumab for zone ii stage 2 retinopathy of prematurity with plus disease., PMID:40377801
Recurrence of Macular Edema in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion-A Comparison of Aflibercept and Ranibizumab in a Randomized Trial., PMID:40373873
Sustainable Practices in Anti-VEGF Therapy: A 15-Year Bibliometric Analysis of Ranibizumab for Age-Related Macular Degeneration., PMID:40365539
Planned vs. Performed Treatment Regimens in Diabetic Macular Edema: Real-World Evidence from the PACIFIC Study., PMID:40364151
Dynamic Changes of Aqueous Matrix Metalloproteinases and Imaging Correlation in Retinal Vein Occlusion Following Ranibizumab Therapy., PMID:40359464
Silicone oil microdroplets from syringes with intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor and complement inhibitor injections., PMID:40359347
OCTA as a reliable prognostic tool for active NVD treated with Panretinal Photocoagulation and/or ranibizumab., PMID:40359330
[Biosimilars of ranibizumab in retinal diseases: new possibilities in ophthalmology]., PMID:40353548
Long-term outcomes of the observe-and-plan regimen in treating neovascular age-related macular degeneration: a retrospective real-life analysis., PMID:40348918
Anti-VEGF drugs compared with laser photocoagulation for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and economic analysis., PMID:40347224
PDVR stage A management: Insights from combined PRP and anti-VEGF treatment outcomes., PMID:40340516
Improved functional and morphological outcomes with faricimab in nAMD eyes with poor response to prior intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy., PMID:40338383
Contributing factors to short-term intraocular pressure elevation following intravitreal anti-VEGF injections., PMID:40335957
Endophthalmitis following intravitreal injections at a tertiary center: real-life data on incidence, risk factors, management strategies, and visual outcomes., PMID:40335933
Visual fields after anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy for retinopathy of prematurity., PMID:40333931
Efficacy of ranibizumab with laser in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy compare with laser monotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis., PMID:40331557
Uncommon Therapeutic Approaches for Patients with Recurrent Central Serous Chorioretinopathy: case report and literature review., PMID:40330964
Predictive factors for adherence to intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in Palestinian patients with diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion, and age-related macular degeneration: a retrospective cohort study., PMID:40329243
Beyond the injection: delivery systems reshaping retinal disease management., PMID:40319468
Real-world safety and efficacy of Anti-VEGF treatment in Brazil., PMID:40298749
Effect of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome on Macular Edema Severity and Response to Intravitreal Ranibizumab in Diabetic Retinopathy and Retinal Vein Occlusion., PMID:40296974
Analysis of the etiology, clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes of choroidal neovascularization in Chinese children and adolescents., PMID:40295924