Catalog No.
KDB95602
Description
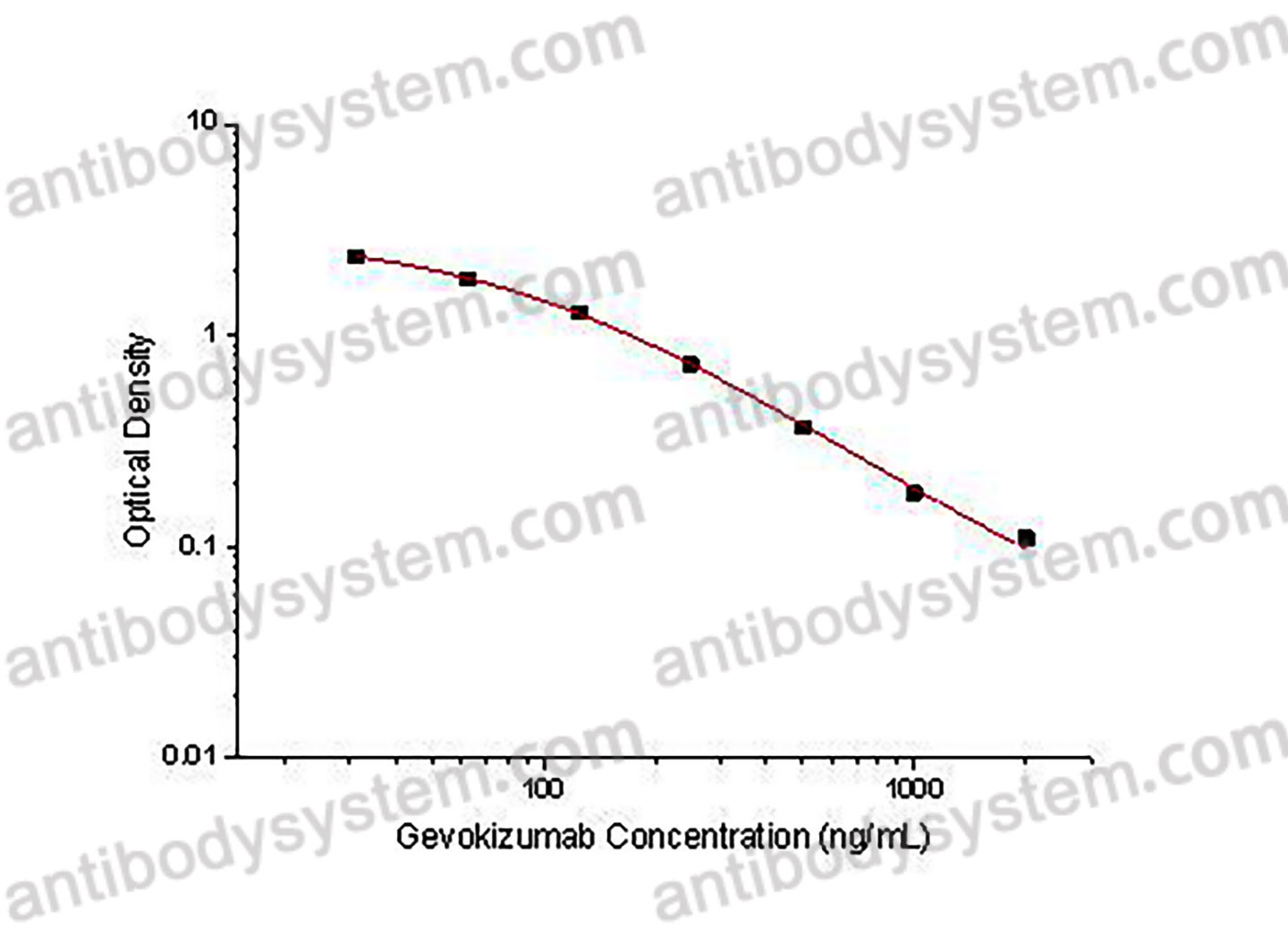
PRINCIPLE OF THE ASSAY
This assay employs the quantitative competitive enzyme immunoassay technique. Recombinant Human IL1B has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards or samples are premixed with biotin-labeled antibody and then pipetted into the wells. Gevokizumab in the sample competitively binds to the pre-coated protein with biotin-labeled Gevokizumab. After washing away any unbound substances, Streptavidin-HRP is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in inversely proportion to the amount of Gevokizumab bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured.
Applications
Used for the quantitative determination of Gevokizumab concentration in serum and plasma.
Detection method
Colorimetric
Sample type
Plasma, Serum
Assay type
Quantitative
Range
31.25 - 2,000 ng/mL
Sensitivity
27.51 ng/mL
Precision
Intra-Assay Precision (Precision within an assay): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested sixteen times on one plate to assess intra-assay precision.
Inter-Assay Precision (Precision between assays): <20%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty four separate assays to assess inter-assay precision.
|
|
Intra-Assay Precision
|
Inter-Assay Precision
|
|
Sample
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
|
n
|
16
|
16
|
16
|
24
|
24
|
24
|
|
Mean (ng/mL)
|
768.3
|
192.7
|
90.0
|
998.8
|
217.3
|
114.9
|
|
Standard deviation
|
49.4
|
11.9
|
5.4
|
141.9
|
43.8
|
21.7
|
|
CV (%)
|
6.4
|
6.2
|
6.0
|
14.2
|
20.1
|
18.9
|
Recovery
80-120%
Shipping
2-8 ℃
Stability and Storage
When the kit was stored at the recommended temperature for 6 months, the signal intensity decreased by less than 20%.
Alternative Names
XOMA 052, CAS: 1129435-60-4
Background
Gevokizumab (XOMA-052) was developed by XOMA Ltd., USA and represents a humanized IgG2kappa antibody. XOMA-052 binds to IL-1β with high affinity leading to reduced binding affinity of the cytokine to its signaling receptor. Since gevokizumab does not influence the affinity of IL-1β for its decoy and soluble inhibitory receptors the endogenous regulatory mechanisms involving the clearance and inhibitory receptors also contribute to the effect of the antibody [6]. In August 2012 the FDA granted orphan drug status to gevokizumab for the treatment of noninfectious intermediate uveitis, posterior uveitis, panuveitis, and chronic noninfectious anterior uveitis. A single intravenous injection of the substance was also shown to lead to complete resolution of intraocular inflammation in Behçet’s uveitis.
A Meta-Analysis Methodology in Stan to Estimate Population Pharmacokinetic Parameters from Multiple Aggregate Concentration-Time Datasets: Application to Gevokizumab mPBPK Model., PMID:39339167
Identification of critical genes and metabolic pathways in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis toward drug repurposing., PMID:39079412
Efficacy and safety of envafolimab in the treatment of advanced dMMR/MSI‑H solid tumors: A single‑arm meta‑analysis., PMID:37545619
Targeting the IL1β Pathway for Cancer Immunotherapy Remodels the Tumor Microenvironment and Enhances Antitumor Immune Responses., PMID:37040466
Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy of IL-1-Targeted Biologics in Treating Immune-Mediated Disorders., PMID:35874710
Current treatment options for monogenic periodic fever syndromes - the role of interleukin 1 inhibitors., PMID:35354288
Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated Episcleritis and Scleritis: An Update on Treatment Perspectives., PMID:34068884
Interleukin-1 Blockade in Polygenic Autoinflammatory Disorders: Where Are We now?, PMID:33708123
IL-1 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Monogenic Periodic Fever Syndromes: From the Past to the Future Perspectives., PMID:33603750
Inhibition of Interleukin-1 in the Treatment of Selected Cardiovascular Complications., PMID:32674739
Biologics in the treatment of pustular psoriasis., PMID:32615817
Biologic therapy for Behçet's uveitis: a systematic review., PMID:31676596
Interleukin-1 blockade treatment decreasing cardiovascular risk., PMID:31415103
Targeting blockade of nuclear factor-κB in the hypothalamus paraventricular nucleus to prevent cardiac sympathetic hyperinnervation post myocardial infarction., PMID:31175933
The right place of interleukin-1 inhibitors in the treatment of Behçet's syndrome: a systematic review., PMID:30799530
Microglial Mincle receptor in the PVN contributes to sympathetic hyperactivity in acute myocardial infarction rat., PMID:30353660
The IL-1β Antibody Gevokizumab Limits Cardiac Remodeling and Coronary Dysfunction in Rats With Heart Failure., PMID:30062160
Interleukin-1 blockade in cardiovascular diseases: a clinical update., PMID:29584915
Use of Gevokizumab in Patients with Behçet's Disease Uveitis: An International, Randomized, Double-Masked, Placebo-Controlled Study and Open-Label Extension Study., PMID:29370572
Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases with IL-1 Blockade., PMID:33133777
Cytokines of the IL-1 family: recognized targets in chronic inflammation underrated in organ transplantations., PMID:28798075
IL-1β Inhibition in Cardiovascular Complications Associated to Diabetes Mellitus., PMID:28659798
Potential of IL-1, IL-18 and Inflammasome Inhibition for the Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases., PMID:28588486
Effect of Gevokizumab on Interleukin-1β-Mediated Cytochrome P450 3A4 and Drug Transporter Repression in Cultured Human Hepatocytes., PMID:28260174
The challenge of autoinflammatory syndromes: with an emphasis on hyper-IgD syndrome., PMID:27856657
One year in review 2016: Behçet's syndrome., PMID:27791958
Interleukin-1 antagonism in type 1 diabetes of long duration., PMID:27720360
Gevokizumab in the Treatment of Autoimmune Non-necrotizing Anterior Scleritis: Results of a Phase I/II Clinical Trial., PMID:27663070
Targeting inflammation in diabetic kidney disease: early clinical trials., PMID:27268955
Cooling down inflammation in type 2 diabetes: how strong is the evidence for cardiometabolic benefit?, PMID:27230767
Safety and Efficacy of Gevokizumab in Patients with Behçet's Disease Uveitis: Results of an Exploratory Phase 2 Study., PMID:26829647
Antibodies to watch in 2016., PMID:26651519
Targeting Interleukin-1 beta to Suppress Sympathoexcitation in Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Hypertensive Rats., PMID:26304161
Giant Cell Arteritis: Beyond Corticosteroids., PMID:26239828
Horizon 2020 in Diabetic Kidney Disease: The Clinical Trial Pipeline for Add-On Therapies on Top of Renin Angiotensin System Blockade., PMID:26239562
Currently Used Biologic Agents in the Management of Behcet's Syndrome., PMID:25666786
Treatment of two patients with generalized pustular psoriasis with the interleukin-1β inhibitor gevokizumab., PMID:25495649
Antibodies to watch in 2015., PMID:25484055
The Use of Biologic Therapies in Uveitis., PMID:25431348
Anti-cytokine biologic treatment beyond anti-TNF in Behçet's disease., PMID:25268669
Effectiveness and tuberculosis-related safety profile of interleukin-1 blocking agents in the management of Behçet's disease., PMID:25151975
The interleukin-1β modulator gevokizumab reduces neointimal proliferation and improves reendothelialization in a rat carotid denudation model., PMID:25108619
Gevokizumab in type 1 diabetes mellitus: extreme remedies for extreme diseases?, PMID:25079039
Biological treatments in Behçet's disease: beyond anti-TNF therapy., PMID:25061259
Emerging therapies for noninfectious uveitis: what may be coming to the clinics., PMID:24868451
Update on the use of systemic biologic agents in the treatment of noninfectious uveitis., PMID:24600203
Antibodies to watch in 2014., PMID:24284914
Detailed mechanistic analysis of gevokizumab, an allosteric anti-IL-1β antibody with differential receptor-modulating properties., PMID:24194526
Current and future treatments for Behçet's uveitis: road to remission., PMID:23729309
Inflammasome and cytokine blocking strategies in autoinflammatory disorders., PMID:23697917