Catalog No.
FHJ56010
Species reactivity
Human
Host species
Mouse
Isotype
IgG1, kappa
Clonality
Monoclonal
Conjugation
Unconjugated
Target
DC-SIGNR, DC-SIGN2, CLEC4M, DC-SIGN-related protein, C-type lectin domain family 4 member M, CD299, L-SIGN, CD209L, Liver/lymph node-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin, CD209L1, Dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing non-integrin 2, CD209 antigen-like protein 1
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Endotoxin level
Please contact with the lab for this information.
Purity
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Purification
Protein A/G purified from cell culture supernatant.
Accession
Q9H2X3
Applications
FCM
Form
Liquid
Storage buffer
0.01M PBS, pH 7.4.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Store at 4°C short term (1-2 weeks). Store at -20°C 12 months. Store at -80°C long term.
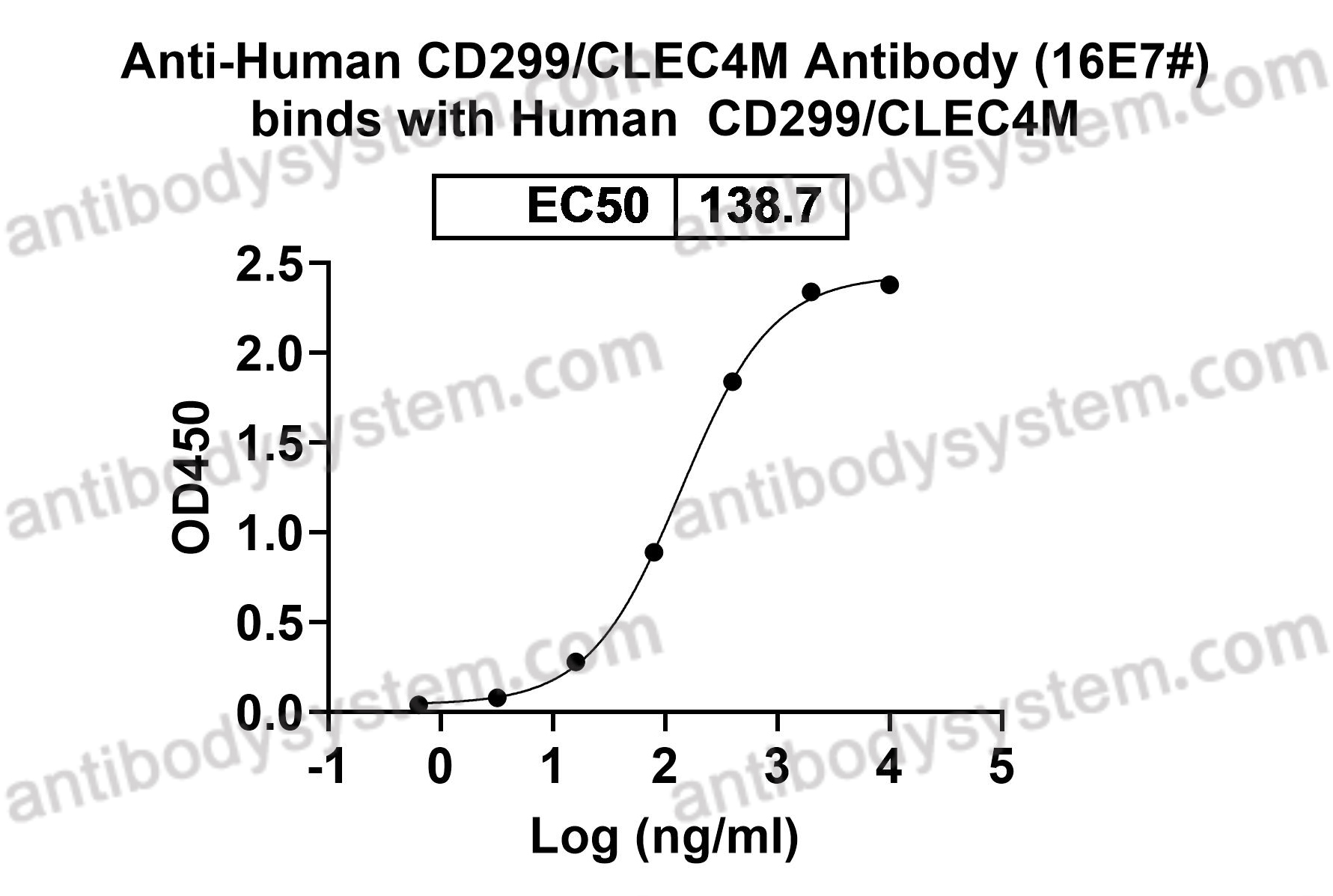
Clone ID
16E7#
Host cell lectins ASGR1 and DC-SIGN jointly with TMEM106B confer ACE2 independence and imdevimab resistance to SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus with spike mutation E484D., PMID:39791910
Simultaneous Blockade of CD209 and CD209L by Monoclonal Antibody Does Not Provide Sufficient Protection Against Multiple Viral Infections In Vivo., PMID:39783143
Lectins enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection and influence neutralizing antibodies., PMID:34464958
Immunohistochemical Study of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Entry Factors in the Cornea and Ocular Surface., PMID:32826650
[Comparative analysis of structural characteristics and epitopes in S proteins between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV]., PMID:32762171
Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of N-glycan Positional Isomers and Evidence for Branch Selective Binding by Monoclonal Antibodies and Human C-type Lectin Receptors., PMID:29894153
CLEC4M-positive and CD81-negative Huh7 cells are not susceptible to JFH-1 HCVcc infection but mediate transinfection., PMID:24965233
Impact of viral attachment factor expression on antibody-mediated neutralization of flaviviruses., PMID:23312596
Interaction of L-SIGN with hepatitis C virus envelope protein E2 up-regulates Raf-MEK-ERK pathway., PMID:23292357
Expression of the C-type lectins DC-SIGN or L-SIGN alters host cell susceptibility for the avian coronavirus, infectious bronchitis virus., PMID:22340967
HIV-1 infection of DC: evidence for the acquisition of virus particles from infected T cells by antigen uptake mechanism., PMID:19829715
Dramatic caspase-dependent apoptosis in antibody-enhanced dengue virus infection of human mast cells., PMID:18809735
The Immunobiology of SARS*., PMID:17243893
DC-SIGN on B lymphocytes is required for transmission of HIV-1 to T lymphocytes., PMID:16839201
Internalizing antibodies to the C-type lectins, L-SIGN and DC-SIGN, inhibit viral glycoprotein binding and deliver antigen to human dendritic cells for the induction of T cell responses., PMID:16365436
Effective induction of naive and recall T-cell responses by targeting antigen to human dendritic cells via a humanized anti-DC-SIGN antibody., PMID:15878980
L-SIGN (CD209L) and DC-SIGN (CD209) mediate transinfection of liver cells by hepatitis C virus., PMID:15371595
Hepatitis C virus targets DC-SIGN and L-SIGN to escape lysosomal degradation., PMID:15254204
C-type lectins L-SIGN and DC-SIGN capture and transmit infectious hepatitis C virus pseudotype particles., PMID:15166245
DC-SIGN and L-SIGN can act as attachment receptors for alphaviruses and distinguish between mosquito cell- and mammalian cell-derived viruses., PMID:14581539
Quantitative expression and virus transmission analysis of DC-SIGN on monocyte-derived dendritic cells., PMID:12186897
Primary isolated human brain microvascular endothelial cells express diverse HIV/SIV-associated chemokine coreceptors and DC-SIGN and L-SIGN., PMID:12083838
Functional evaluation of DC-SIGN monoclonal antibodies reveals DC-SIGN interactions with ICAM-3 do not promote human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmission., PMID:12021323
Expression of DC-SIGN by dendritic cells of intestinal and genital mucosae in humans and rhesus macaques., PMID:11799181