Catalog No.
YVV19201
Expression system
E. coli
Species
Coxsackievirus A16 (strain Tainan/5079/98)
Protein length
Gly566-Leu862
Predicted molecular weight
33.94 kDa
Nature
Recombinant
Endotoxin level
Please contact with the lab for this information.
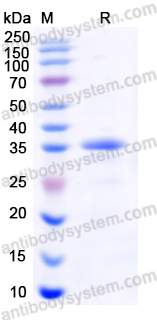
Purity
>90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
Accession
Q9QF31
Applications
ELISA, Immunogen, SDS-PAGE, WB, Bioactivity testing in progress
Form
Lyophilized
Storage buffer
Lyophilized from a solution in PBS pH 7.4, 0.02% SKL, 1mM EDTA, 4% Trehalose, 1% Mannitol.
Reconstitution
Reconstitute in sterile water for a stock solution.
Shipping
In general, proteins are provided as lyophilized powder/frozen liquid. They are shipped out with dry ice/blue ice unless customers require otherwise.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Store at 2 to 8°C for frequent use. Store at -20 to -80°C for twelve months from the date of receipt.
Alternative Names
Genome polyprotein, Virion protein 1, VP1
Cellular response, persistent humoral response and efficacy elicited by a CV-A16 vaccine candidate in mice., PMID:40499348
The Emergence of Coxsackievirus A16 Subgenotype B1c: A Key Driver of the Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease Epidemic in Guangdong, China., PMID:40006974
Metformin inhibits EV-A71 and CVA16 infections by regulating TRIB3-SCARB2 axis and activating AMPK., PMID:39826812
Discovery of a broad-spectrum monoclonal antibody recognizing a conserved, linear epitope WFYDGYPT on VP1 protein of Enterovirus A species., PMID:39736634
Antiviral activity of povidone-iodine gargle and mouthwash solution against Enterovirus A71, Coxsackieviruses A16, A10 and A6., PMID:39548776
Novel virulence determinants in VP1 regulate the assembly of enterovirus-A71., PMID:39535185
Characterization of cross-reactivity of coxsackievirus A2 VP1-specific polyclonal antibodies with enterovirus A71, coxsackievirus A16, and coxsackievirus A6., PMID:39298881
Immunogenicity of trivalent DNA vaccine candidate encapsulated in Chitosan-TPP nanoparticles against EV-A71 and CV-A16., PMID:39140594
First detection of multiple cases related to CV-A16 strain of B1c clade in Beijing in 2022., PMID:38982764
A multiplex one-step fluorescence quantitative differential diagnosis method for severe hand, foot and mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A16., PMID:38901646
Immunogenicity and immunodominant linear B-cell epitopes of a new DNA-based tetravalent vaccine against four major enteroviruses causing hand, foot, and mouth disease., PMID:38705805
Identification of fangchinoline as a broad-spectrum enterovirus inhibitor through reporter virus based high-content screening., PMID:38452856
Molecular Epidemiology and Evolution of Coxsackievirus A14., PMID:38140564
Molecular epidemiology of hand, foot, and mouth disease in Karnataka, India in 2022., PMID:37945122
An enterovirus A71 virus-like particle with replaced loops confers partial cross-protection in mice., PMID:37788720
Epidemiology of Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease and Genetic Evolutionary Characteristics of Coxsackievirus A10 in Taiyuan City, Shanxi Province from 2016 to 2020., PMID:36992403
The upregulation of peripheral blood polyamine metabolites spermidine and spermine in children with hand, foot, mouth disease is related to enterovirus 71 capsid protein VP1, but not VP4., PMID:36891375
Coxsackievirus A6 Infection Causes Neurogenic Pathogenesis in a Neonatal Murine Model., PMID:36851724
Clinical profile and molecular typing of viral etiological agents associated with Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD): A study from Udhampur, Northern India., PMID:36470773
Identification of a neutralizing linear epitope within the VP1 protein of coxsackievirus A10., PMID:36457099
Epidemiology of hand, foot, and mouth disease and the genetic characteristics of Coxsackievirus A16 in Taiyuan, Shanxi, China from 2010 to 2021., PMID:36439232
Genetic and Cross Neutralization Analyses of Coxsackievirus A16 Circulating in Taiwan from 1998 to 2021 Suggest Dominant Genotype B1 can Serve as Vaccine Candidate., PMID:36298861
Cryo-electron microscopy and image classification reveal the existence and structure of the coxsackievirus A6 virion., PMID:36056184
Development of stable, cold-adapted, temperature-sensitive/conditional lethal chimeric enterovirus A71 and coxsackievirus A16., PMID:35964922
Development and evaluation of an inactivated coxsackievirus A16 vaccine in gerbils., PMID:35787233
Recovery Infectious Enterovirus 71 by Bac-to-Bac Expression System in vitro and in vivo., PMID:35356523
Molecular epidemiology of coxsackievirus A16 circulating in children in Beijing, China from 2010 to 2019., PMID:34453285
First evidence of enterovirus A71 and echovirus 30 in Uruguay and genetic relationship with strains circulating in the South American region., PMID:34383835
[Preparation of pan-neutralizing mouse monoclonal antibodies against enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16]., PMID:34140076
Chimeric enterovirus 71 virus-like particle displaying conserved coxsackievirus A16 epitopes elicits potent immune responses and protects mice against lethal EV71 and CA16 infection., PMID:34116877
Genetic analysis of Enterovirus D68 associated with pneumonia in children from South India., PMID:33999799
SAMHD1 Inhibits Multiple Enteroviruses by Interfering with the Interaction between VP1 and VP2 Proteins., PMID:33883225
Viral determinants that drive Enterovirus-A71 fitness and virulence., PMID:33745413
Co-circulation of coxsackieviruses A-6, A-10, and A-16 causes hand, foot, and mouth disease in Guangzhou city, China., PMID:32264839
Coxsackievirus A6 Induces Necroptosis for Viral Production., PMID:32117097
Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Novel Enterovirus 71 Inhibitors as Therapeutic Drug Leads for the Treatment of Human Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease., PMID:31939669
National Epidemiology and Evolutionary History of Four Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease-Related Enteroviruses in China from 2008 to 2016., PMID:31664644
Molecular epidemiology of enterovirus from children with herpangina or hand, foot, and mouth disease in Hangzhou, 2016., PMID:31321585
Enterovirus type 71-immunized chicken egg yolk immunoglobulin has cross antiviral activity against coxsackievirus A16 in vitro., PMID:31258670
The surveillance of the epidemiological and serotype characteristics of hand, foot, mouth disease in Neijiang city, China, 2010-2017: A retrospective study., PMID:31170178
In Vitro and In Vivo Inhibition of the Infectivity of Human Enterovirus 71 by a Sulfonated Food Azo Dye, Brilliant Black BN., PMID:31167919
Recombinant CV-A6 strains related to hand-foot-mouth disease and herpangina at primary care centers (Barcelona, Spain)., PMID:31033351
Molecular characteristic analysis for the VP1 region of coxsackievirus A6 strains isolated in Jiujiang area, China, from 2012 to 2013., PMID:30946358
A potential therapeutic neutralization monoclonal antibody specifically against multi-coxsackievirus A16 strains challenge., PMID:30735461
Surveillance for severe hand, foot, and mouth disease from 2009 to 2015 in Jiangsu province: epidemiology, etiology, and disease burden., PMID:30669973
Spiramycin and azithromycin, safe for administration to children, exert antiviral activity against enterovirus A71 in vitro and in vivo., PMID:30599241
Molecular surveillance of coxsackievirus A16 reveals the emergence of a new clade in mainland China., PMID:30498962
Genetic characteristics of the P1 coding region of Coxsackievirus A16 associated with hand, foot, and mouth disease in China., PMID:30182173
Molecular characterization of Coxsackievirus A16 strains isolated from children with severe hand, foot, and mouth disease in Yunnan, Southwest China, during 2009-2015., PMID:30168582
Molecular characteristics of hand, foot, and mouth disease for hospitalized pediatric patients in Yunnan, China., PMID:30075535