Catalog No.
PHF93601
Species reactivity
Human, Mouse
Host species
Rabbit
Isotype
IgG
Clonality
Polyclonal
Immunogen
E. coli - derived recombinant Human COL7A1 (Leu2785-Asp2944).
Tested applications
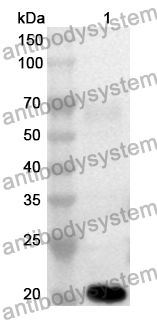
ELISA: 1:4000-1:8000, IHC: 1:50-1:100, WB: 1:1000-1:4000
Target
Long-chain collagen, Collagen alpha-1(VII) chain, COL7A1, LC collagen
Purification
Purified by antigen affinity column.
Accession
Q02388
Applications
ELISA, IHC, WB
Form
Liquid
Storage buffer
0.01M PBS, pH 7.4, 50% Glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Store at 2 to 8°C for frequent use. Store at -20 to -80°C for twelve months from the date of receipt.
Good clinical response to cemiplimab in a young patient with locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma on preexisting recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:38808531
Dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa is associated with glycolytically active GATA3+ T helper 2 cells which may contribute to pruritus in lesional skin., PMID:38477474
Intravenous gentamicin therapy induces functional type VII collagen in patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: an open-label clinical trial., PMID:38366625
Identification of a novel COL7A1 variant associated with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa responding effectively to dupilumab., PMID:37676173
Case report: bullous pemphigoid development underlies dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa disease worsening., PMID:35967298
Glomerular IgA Deposition and Serum Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody Positivity in a Child With Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa: Case Report and Literature Review., PMID:35899130
Case Report: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenges in Severe Mechanobullous Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita., PMID:35464429
In vivo topical gene therapy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: a phase 1 and 2 trial., PMID:35347281
hTERT-Driven Immortalization of RDEB Fibroblast and Keratinocyte Cell Lines Followed by Cre-Mediated Transgene Elimination., PMID:33916959
A Case of Dominant Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa with a G2043R Mutation in the Type VII Collagen Gene., PMID:33835003
Self-improving dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: First report of clinical, molecular, and genetic characterization of five patients from Southeast Asia., PMID:33258232
Promising effect of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa., PMID:32506551
Pembrolizumab for Treatment of a Patient With Multiple Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa., PMID:32320041
Murine type VII collagen distorts outcome in human skin graft mouse model for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:30019435
Efficacy of Human Placental-Derived Stem Cells in Collagen VII Knockout (Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa) Animal Model., PMID:29745997
Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB) Acquisita in an Adult Patient with Previously Unrecognized Mild Dystrophic EB and Biallelic COL7A1 Mutations., PMID:29182795
Gentamicin induces functional type VII collagen in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa patients., PMID:28691931
Nonsense variant in COL7A1 causes recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in Central Asian Shepherd dogs., PMID:28493971
Correction of Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa by Transposon-Mediated Integration of COL7A1 in Transplantable Patient-Derived Primary Keratinocytes., PMID:28027893
T cells mediate autoantibody-induced cutaneous inflammation and blistering in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita., PMID:27917914
A Gene Gun-mediated Nonviral RNA trans-splicing Strategy for Col7a1 Repair., PMID:26928235
Canakinumab in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: a novel unexpected weapon for non-healing wounds?, PMID:26885873
Reduced Toxicity Conditioning and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Transplantation for Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa., PMID:26148662
Mechanisms of natural gene therapy in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:24577406
De novo anti-type VII collagen antibodies in patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:24213372
Prevalence of specific anti-skin autoantibodies in a cohort of patients with inherited epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:24007552
Epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa: a case with prominent histopathologic inflammation., PMID:23616197
Gene expression signatures of mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the cutaneous environment and therapeutic implications for blistering skin disorder., PMID:20854215
Bone marrow transplantation for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:20818854
Keratinocyte-/fibroblast-targeted rescue of Col7a1-disrupted mice and generation of an exact dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa model using a human COL7A1 mutation., PMID:19893033
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa phenotypes in a large consanguineous Tunisian family., PMID:19261445
Injection of recombinant human type VII collagen corrects the disease phenotype in a murine model of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:19018253
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa in Italy: clinical and molecular characterization., PMID:16965329
Transient bullous dermolysis of the newborn in three generations., PMID:16225626
Two novel heterozygous mutations in COL7A1 in a Chinese patient with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa of Hallopeau-Siemens type., PMID:15949010
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa inversa with COL7A1 mutations and absence of GDA-J/F3 protein., PMID:12787275
Characterization of mutations of the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa mitis (M-RDEB) from three Korean patients., PMID:11378329
Tissue-specific expression and long-term deposition of human collagen VII in the skin of transgenic mice: implications for gene therapy., PMID:11083471
Pretibial dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: a recessively inherited COL7A1 splice site mutation affecting procollagen VII processing., PMID:10583163
Reduced anchoring fibril formation and collagen VII immunoreactivity in feline dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:10568446
Targeted inactivation of the type VII collagen gene (Col7a1) in mice results in severe blistering phenotype: a model for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:10523500
Moderation of phenotypic severity in dystrophic and junctional forms of epidermolysis bullosa through in-frame skipping of exons containing non-sense or frameshift mutations., PMID:10469327
Three homozygous PTC mutations in the collagen type VII gene of patients affected by recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: analysis of transcript levels in dermal fibroblasts., PMID:10408773
Biology of anchoring fibrils: lessons from dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:10367730
Smad-dependent transcriptional activation of human type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) promoter by transforming growth factor-beta., PMID:9582342
Genetic basis of dominantly inherited transient bullous dermolysis of the newborn: a splice site mutation in the type VII collagen gene., PMID:9406826
Immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and molecular features of Kindler syndrome distinguish it from dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa., PMID:9301588
Premature termination codon mutations in the type VII collagen gene in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa result in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay and absence of functional protein., PMID:9284110
A combination of a common splice site mutation and a frameshift mutation in the COL7A1 gene: absence of functional collagen VII in keratinocytes and skin., PMID:9284109