Catalog No.
PHE73701
Species reactivity
Human
Host species
Rabbit
Isotype
IgG
Clonality
Polyclonal
Immunogen
E. coli - derived recombinant Human LIG4 (Met1-Lys609).
Tested applications
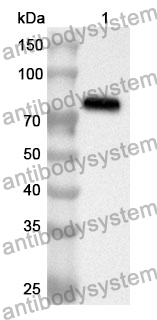
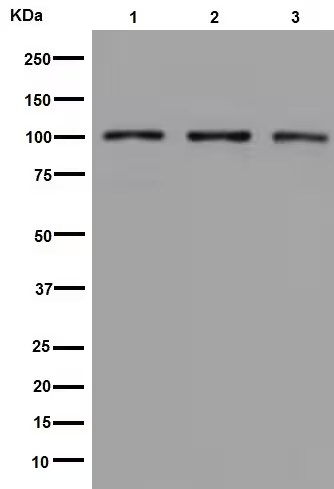
ELISA: 1:4000-1:8000, IHC: 1:50-1:100, WB: 1:1000-1:4000
Target
DNA ligase IV, Polydeoxyribonucleotide synthase [ATP] 4, LIG4, DNA ligase 4
Purification
Purified by antigen affinity column.
Accession
P49917
Applications
ELISA, IHC, WB
Form
Liquid
Storage buffer
0.01M PBS, pH 7.4, 50% Glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Store at 2 to 8°C for frequent use. Store at -20 to -80°C for twelve months from the date of receipt.
DNA Ligase 4 Inhibition Sensitizes Prostate Cancer to Immune Checkpoint Blockade In Vivo., PMID:40037856
DNA ligase IV dificiency with elevated serum IgG levels suspected to have myelodysplastic syndrome: a case report., PMID:36221079
Multiple DSB Resection Activities Redundantly Promote Alternative End Joining-Mediated Class Switch Recombination., PMID:34926456
X-ray scattering reveals disordered linkers and dynamic interfaces in complexes and mechanisms for DNA double-strand break repair impacting cell and cancer biology., PMID:34056803
Precision medicine phase II study evaluating the efficacy of a double immunotherapy by durvalumab and tremelimumab combined with olaparib in patients with solid cancers and carriers of homologous recombination repair genes mutation in response or stable after olaparib treatment., PMID:32778095
Genetic interaction between the non-homologous end-joining factors during B and T lymphocyte development: In vivo mouse models., PMID:32654175
Intra-Vκ Cluster Recombination Shapes the Ig Kappa Locus Repertoire., PMID:31875554
Generation of a Mouse Model Lacking the Non-Homologous End-Joining Factor Mri/Cyren., PMID:31795137
Effects of DNA end configuration on XRCC4-DNA ligase IV and its stimulation of Artemis activity., PMID:28696258
XLF deficiency results in reduced N-nucleotide addition during V(D)J recombination., PMID:27281794
The DNA Ligase IV Syndrome R278H Mutation Impairs B Lymphopoiesis via Error-Prone Nonhomologous End-Joining., PMID:26608917
Organization and dynamics of the nonhomologous end-joining machinery during DNA double-strand break repair., PMID:25941401
Phosphorylated Sp1 is the regulator of DNA-PKcs and DNA ligase IV transcription of daunorubicin-resistant leukemia cell lines., PMID:24530422
ID1 affects the efficacy of radiotherapy in glioblastoma through inhibition of DNA repair pathways., PMID:23377983
Arabidopsis ARP endonuclease functions in a branched base excision DNA repair pathway completed by LIG1., PMID:21781197
Competition between PARP-1 and Ku70 control the decision between high-fidelity and mutagenic DNA repair., PMID:21256093
Widespread dependence of backup NHEJ on growth state: ramifications for the use of DNA-PK inhibitors., PMID:20950945
Alternative end-joining catalyzes class switch recombination in the absence of both Ku70 and DNA ligase 4., PMID:20142431
Homozygous DNA ligase IV R278H mutation in mice leads to leaky SCID and represents a model for human LIG4 syndrome., PMID:20133615
Inter-individual variation in DNA double-strand break repair in human fibroblasts before and after exposure to low doses of ionizing radiation., PMID:19896956
Association between total immunoglobulin E and antibody responses to naturally acquired Ascaris lumbricoides infection and polymorphisms of immune system-related LIG4, TNFSF13B and IRS2 genes., PMID:19604268
Impaired lymphocyte development and antibody class switching and increased malignancy in a murine model of DNA ligase IV syndrome., PMID:19451691
The human set and transposase domain protein Metnase interacts with DNA Ligase IV and enhances the efficiency and accuracy of non-homologous end-joining., PMID:18773976
Human DNA ligases I and III, but not ligase IV, are required for microhomology-mediated end joining of DNA double-strand breaks., PMID:18440984
IgH class switching and translocations use a robust non-classical end-joining pathway., PMID:17713479
A severe form of human combined immunodeficiency due to mutations in DNA ligase IV., PMID:16585603
Severe combined immunodeficiency and microcephaly in siblings with hypomorphic mutations in DNA ligase IV., PMID:16358361
Both V(D)J coding ends but neither signal end can recombine at the bcl-2 major breakpoint region, and the rejoining is ligase IV dependent., PMID:16024785
Impact of DNA ligase IV on nonhomologous end joining pathways during class switch recombination in human cells., PMID:15657289
A Rad50-dependent pathway of DNA repair is deficient in Fanconi anemia fibroblasts., PMID:15199173
Biochemical evidence for Ku-independent backup pathways of NHEJ., PMID:12954774
In vitro and in vivo interactions of DNA ligase IV with a subunit of the condensin complex., PMID:12589063
Identification of human autoantibodies to the DNA ligase IV/XRCC4 complex and mapping of an autoimmune epitope to a potential regulatory region., PMID:12218164
Autoantibodies against DNA double-strand break repair proteins., PMID:11689355
Genetic evidence for the involvement of DNA ligase IV in the DNA-PK-dependent pathway of non-homologous end joining in mammalian cells., PMID:11292837
Late embryonic lethality and impaired V(D)J recombination in mice lacking DNA ligase IV., PMID:9823897
DNA ligase IV from HeLa cell nuclei., PMID:8798671
Monoclonal antibodies recognising differentiation antigens on porcine B cells., PMID:7856057