Catalog No.
PHK39301
Species reactivity
Human
Host species
Rabbit
Isotype
IgG
Clonality
Polyclonal
Immunogen
E. coli - derived recombinant Human ATOH1 (Ser150-Thr217).
Tested applications
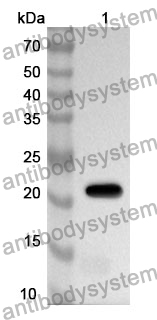
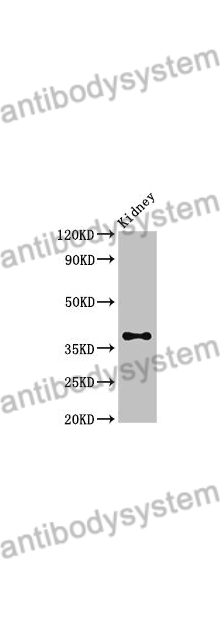
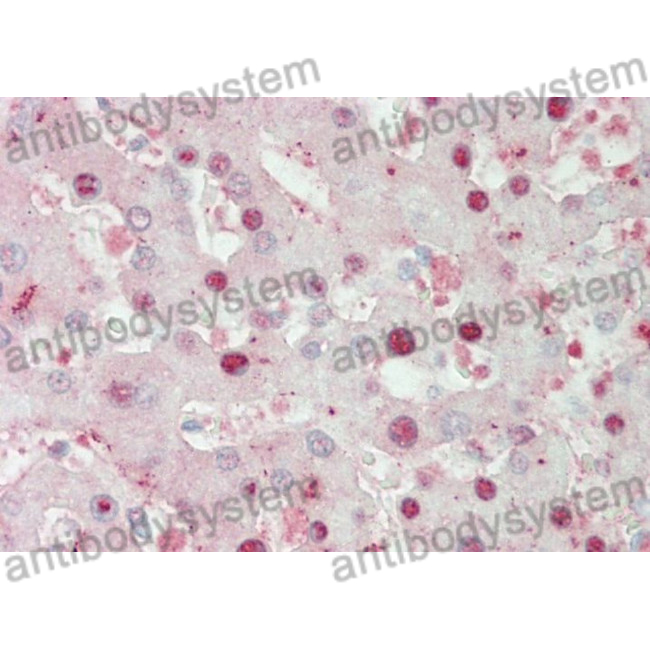
ELISA: 1:4000-1:8000, IHC: 1:50-1:100, WB: 1:1000-1:4000
Target
Helix-loop-helix protein hATH-1, BHLHA14, Class A basic helix-loop-helix protein 14, ATOH1, ATH1, Protein atonal homolog 1, bHLHa14, hATH1
Purification
Purified by antigen affinity column.
Accession
Q92858
Applications
ELISA, IHC, WB
Form
Liquid
Storage buffer
0.01M PBS, pH 7.4, 50% Glycerol, 0.05% Proclin 300.
Stability and Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Store at 2 to 8°C for frequent use. Store at -20 to -80°C for twelve months from the date of receipt.
Administration of cyclophosphamide to rats induces pica and potentiates 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis in the intestine without causing severe intestinal injury., PMID:34507634
Characterization of spatial and temporal development of Type I and Type II hair cells in the mouse utricle using new cell-type-specific markers., PMID:30455179
Multiple zebrafish atoh1 genes specify a diversity of neuronal types in the zebrafish cerebellum., PMID:29548943
The role of Gαq/Gα11 signaling in intestinal epithelial cells., PMID:29387814
Requirement of Gαq/Gα11 Signaling in the Preservation of Mouse Intestinal Epithelial Homeostasis., PMID:28174748
Hair cell regeneration or the expression of related factors that regulate the fate specification of supporting cells in the cochlear ducts of embryonic and posthatch chickens., PMID:26688175
In Vivo Cochlear Hair Cell Generation and Survival by Coactivation of β-Catenin and Atoh1., PMID:26224861
Embryonic maturation of epidermal Merkel cells is controlled by a redundant transcription factor network., PMID:25468937
In vivo generation of immature inner hair cells in neonatal mouse cochleae by ectopic Atoh1 expression., PMID:24586731
[Transdifferention of some supporting cells in the cochlea induced by Ad5 atoh1/EGFP in the young adult guinea pigs]., PMID:22870721
NOTCH Signaling and ATOH1 in Colorectal Cancers., PMID:21980310
Molecular characterization of the mouse superior lateral parabrachial nucleus through expression of the transcription factor Runx1., PMID:21085653
Neurod1 suppresses hair cell differentiation in ear ganglia and regulates hair cell subtype development in the cochlea., PMID:20661473
Expression of Reg IV and Hath1 in neuroendocrine neoplasms., PMID:19924642
Epidermal progenitors give rise to Merkel cells during embryonic development and adult homeostasis., PMID:19786578
Epithelial stem cell-related alterations in Trichinella spiralis-infected small intestine., PMID:19397593
Voltage-activated ion channels and Ca(2+)-induced Ca (2+) release shape Ca (2+) signaling in Merkel cells., PMID:18415122
Cooperation between the Hic1 and Ptch1 tumor suppressors in medulloblastoma., PMID:18347096
The α1 subunit of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the inner ear: transcriptional regulation by ATOH1 and co-expression with the γ subunit in hair cells., PMID:17961150
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are progenitors in vitro for inner ear hair cells., PMID:17113786
Mapping of notch activation during cochlear development in mice: implications for determination of prosensory domain and cell fate diversification., PMID:16736472
A novel role for the choroid plexus in BMP-mediated inhibition of differentiation of cerebellar neural progenitors., PMID:16325379
Crossinhibitory activities of Ngn1 and Math1 allow specification of distinct dorsal interneurons., PMID:11502254
Regulated expression of neurogenic basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors during differentiation of the immortalized neuronal progenitor cell line HC2S2 into neurons., PMID:9634594