In December 2025, multiple AntibodySystem products were cited in high-impact international journals, including Nature Communications and Advanced Science. These studies span cutting-edge research the pathogenicity and immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 JN.1-derived variants, anti-tumor mechanisms of marine terpenoids targeting UBE2C, development of influenza/COVID-19 hybrid vaccines, regulation of erythropoiesis, and precision vaccine design for osteoporosis.
From monoclonal antibodies such as Pemivibart and Romosozumab to recombinant UBE2C protein, AntibodySystem products provided essential tools for molecular mechanism elucidation, therapeutic target validation, and the development of novel preventive and therapeutic strategies across virology, oncology, and vaccine research. AntibodySystem remains committed to supporting global research communities and advancing life science discoveries from fundamental research to translational applications. Today, let’s explore a selection of publications newly citing AntibodySystem products in December, together with Dr. Connie.
Title:
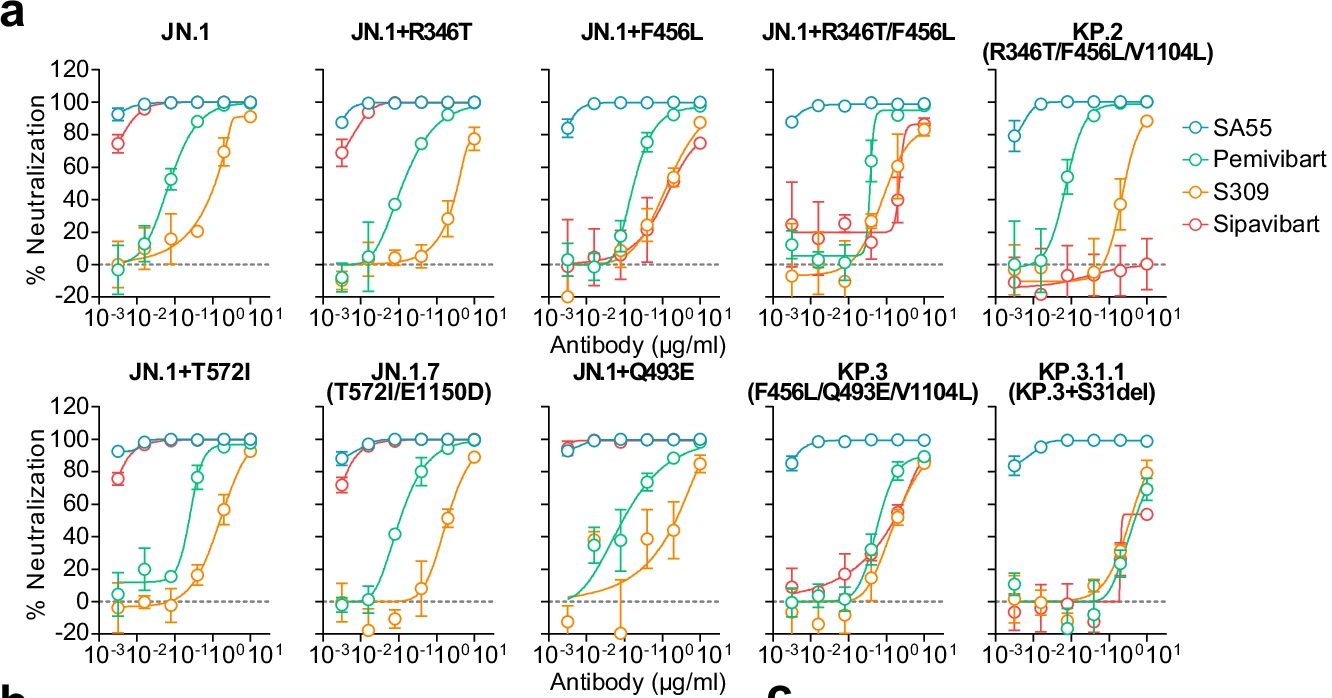
Pathogenicity, virological features, and immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 JN.1-derived variants including JN.1.7, KP.2, KP.3, and KP.3.1.1
DOI:
10.1038/s41467-025-66018-x

Key finding:
The microtubule inhibitor KY216 suppresses non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) metastasis by selectively binding to curved tubulin and targeting vasohibin-2 (VASH2). The study demonstrates that KY216 not only downregulates VASH2 expression but also promotes its interaction with α-tubulin, thereby inhibiting ZEB1 activation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). In parallel, KY216 upregulates miR-429, which cooperatively suppresses metastasis by targeting the VASH2/ZEB1 axis. Collectively, this work uncovers a previously unrecognized mechanism by which microtubule-targeting agents inhibit tumor metastasis.
Cited Product:
DVV00353, Research Grade Sipavibart

Application in the Study:
AntibodySystem’s Research Grade Sipavibart (Cat. No. DVV00353) was used in pseudovirus neutralization assays to evaluate its neutralizing potency against JN.1-derived variants. The resulting data provided critical insights into the immune evasion properties of these emerging variants.
Title:
KY216-tubulin complex captures VASH2 to inhibit NSCLC metastasis
DOI:
10.1038/s41467-025-66817-2

Key finding:
The microtubule inhibitor KY216 suppresses non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) metastasis by selectively binding to curved tubulin and targeting vasohibin-2 (VASH2). The study demonstrates that KY216 not only downregulates VASH2 expression but also promotes its interaction with α-tubulin, thereby inhibiting ZEB1 activation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). In parallel, KY216 upregulates miR-429, which cooperatively suppresses metastasis by targeting the VASH2/ZEB1 axis. Collectively, this work uncovers a previously unrecognized mechanism by which microtubule-targeting agents inhibit tumor metastasis.
Cited Product:
YHK84701, Recombinant Human VASH2/Vasohibin-2 Protein, N-His-SUMO

Application in the Study:
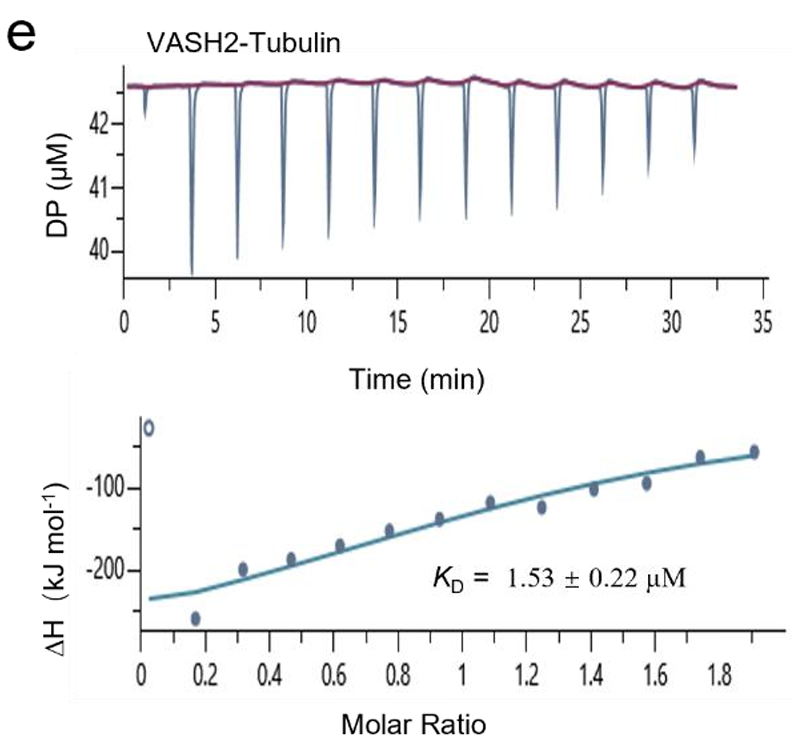
AntibodySystem’s Recombinant Human VASH2/Vasohibin-2 Protein, N-His-SUMO (Cat. No. YHK84701) was used in isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) assays to demonstrate that the microtubule inhibitor KY216 markedly enhances the interaction between VASH2 and tubulin. The presence of KY216 increased the binding affinity by approximately 2.9-fold and reduced the Gibbs free energy of the interaction. These results provide critical molecular interaction evidence that KY216 suppresses metastasis by stabilizing the VASH2–tubulin complex, promoting α-tubulin detyrosination, and inhibiting ZEB1 activity.
Title:
Halorotetin B, A Novel Terpenoid Compound Derived from Marine Ascidian, Suppresses Tumor Growth by Targeting the Cell Cycle Regulator UBE2C
DOI:
10.1038/s41467-025-66018-x
Key finding:
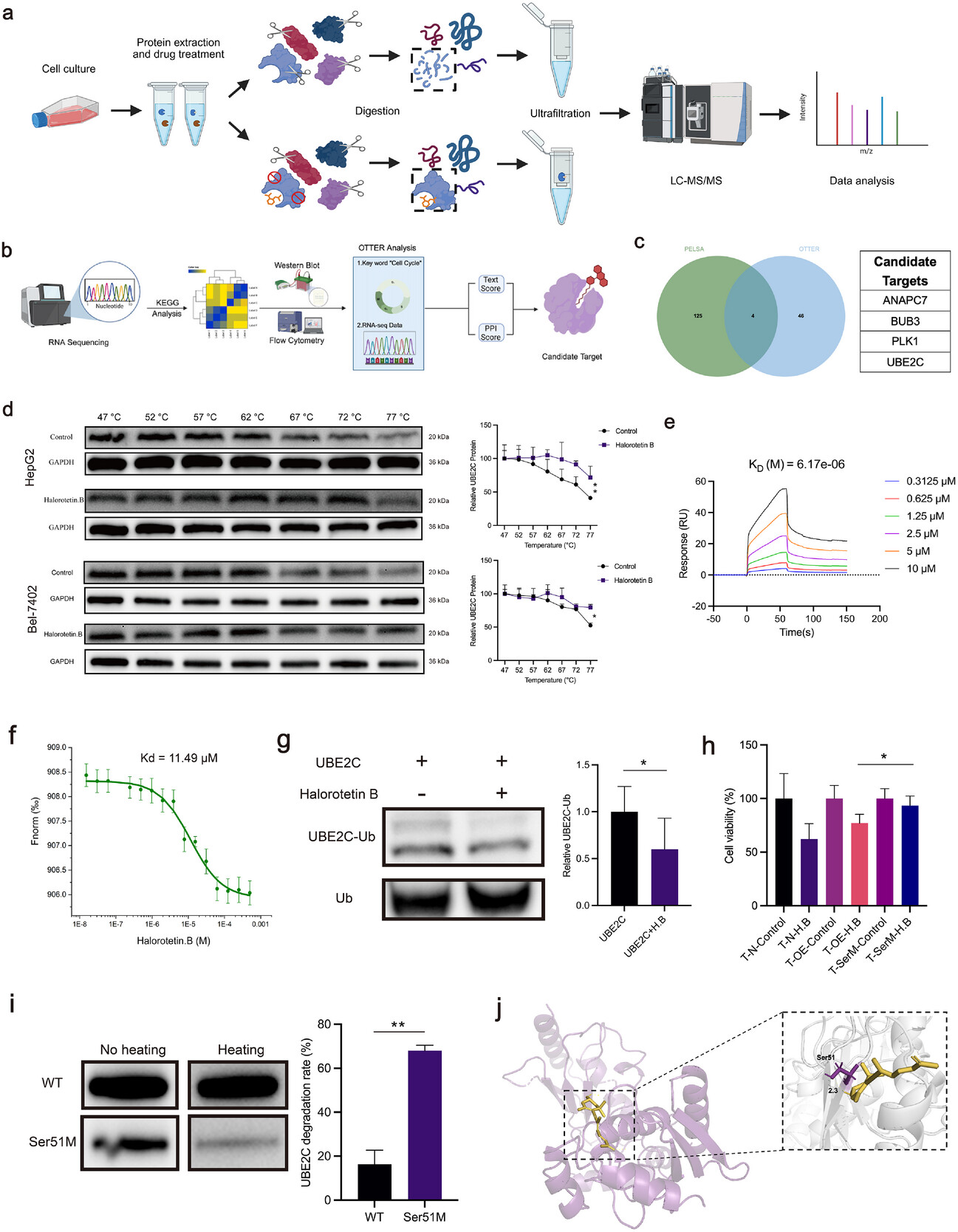
This study identifies Halorotetin B, a novel terpenoid isolated from edible ascidians, as a potent tumor growth inhibitor. Mechanistically, Halorotetin B directly targets the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UBE2C, inhibiting the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cyclin B1 and securin. This leads to M-phase arrest and cellular senescence in tumor cells, offering a promising strategy for developing ascidian-derived anticancer agents targeting UBE2C.
Cited Product:
YHA19001, Recombinant Human UBE2C Protein, N-His

Application in the Study:
AntibodySystem’s Recombinant Human UBE2C Protein, N-His (Cat. No. YHA19001) was used in microscale thermophoresis (MST) assays to confirm direct binding between Halorotetin B and UBE2C, with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 11.49 μM. This result provided key molecular interaction evidence supporting the proposed anti-tumor mechanism.
Title:
Ferritin-based hybrid protein particle vaccine combining M2e antigen of influenza A virus and S-protein tandem epitopes of SARS-CoV-2
DOI:
10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.149867
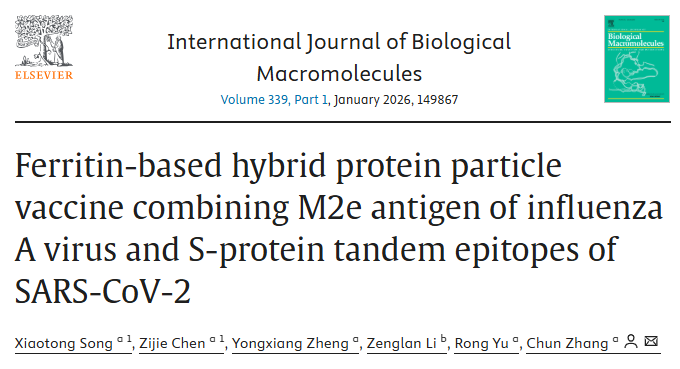
Key finding:
This study presents a hybrid protein particle vaccine based on human ferritin heavy chain. Influenza A virus M2e and SARS-CoV-2 spike tandem epitopes (STE) were expressed separately in E. coli and co-assembled into hybrid particles. In mice, the vaccine elicited significantly enhanced antibody responses, effectively inhibited SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus infection, and mediated ADCC activity, demonstrating strong potential for combined viral prevention.
Cited Product:
RVV23403, Anti-Influenza A virus M2 ectodomain/M2e Antibody (Fab65)

Application in the Study:
AntibodySystem’s Anti-Influenza A Virus M2 Ectodomain/M2e Antibody (Fab65)(Cat. No. RVV23403) was used in confocal microscopy to validate surface expression of M2 protein on 293T-M2 cells, providing a foundation for subsequent functional evaluation of M2e-specific antibodies in immunized sera.
Title:
Prpf4 sequentially regulates the expansion and maturation of erythrocyte through distinct mechanisms
DOI:
10.1038/s41420-025-02846-6

Key finding:
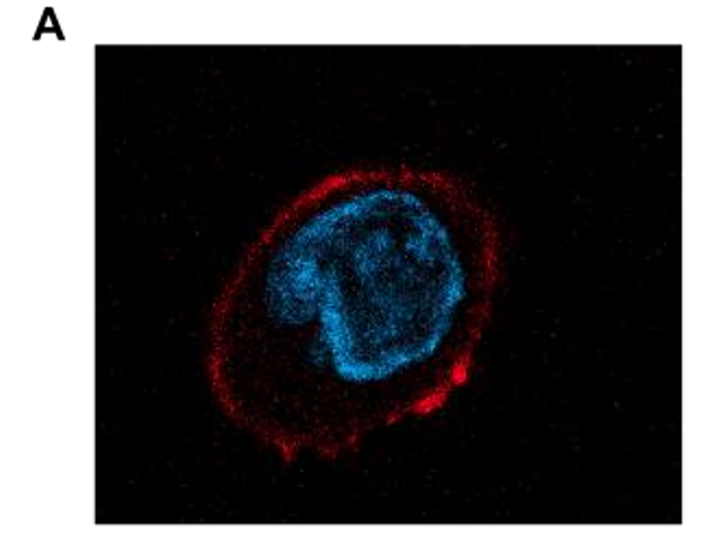
This study reveals that Prpf4 sequentially regulates early proliferation and late maturation during zebrafish erythropoiesis. Loss of Prpf4 results in reduced erythrocyte numbers and impaired maturation by inducing DNA damage and activating the ATM/Chk2–p53 pathway to suppress proliferation, while simultaneously causing splicing defects of slc25a39 that compromise maturation. These findings elucidate the coordinated regulation of erythroid development.
Cited Product:
RGK60001, Anti-DNA-RNA Hybrid Antibody(S9.6)

Application in the Study:
AntibodySystem’s Anti-DNA–RNA Hybrid Antibody (S9.6) (Cat. No. RGK60001) was used in Western blot analyses to demonstrate R-loop accumulation in erythroid progenitors following Prpf4 loss of function, providing critical molecular evidence for activation of the DNA damage response pathway.
Title:
In silico design of novel precision vaccine targeting sclerostin epitopes for osteoporosis prevention and treatment
DOI:
10.3389/fimmu.2025.1644437

Key finding:
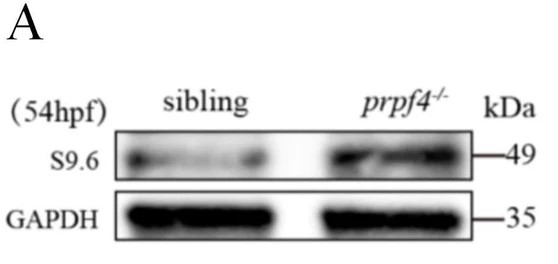
This study reports the development of a novel osteoporosis vaccine targeting sclerostin (SOST). Based on the high-affinity SOST131–163 epitope recognized by Romosozumab, the epitope was fused to a diphtheria toxin translocation domain to overcome immune tolerance and induce high-titer antibodies in mice. The elicited antibodies inhibited osteoclast differentiation and promoted osteoblast mineralization, offering a cost-effective strategy for early prevention and long-term treatment of osteoporosis.
Cited Product:
DHJ48701, Research Grade Romosozumab

Application in the Study:
AntibodySystem’s Research Grade Romosozumab (Cat. No. DHJ48701) was used in ELISA assays to confirm SOST131–163 as a high-affinity binding epitope, supporting the mechanistic basis for epitope-based precision vaccine design.
Title:
Demyelination and Cognitive Performance in Long COVID Patients with Insomnia and/or Depression
DOI:
10.3390/ijms262412141

Key finding:
This study demonstrates that insomnia and depressive symptoms in long COVID patients are associated with distinct cognitive impairments and patterns of white matter demyelination. Patients with insomnia exhibited the most pronounced global cognitive and executive dysfunction, accompanied by widespread demyelination, while patients with depression showed deficits primarily in attention-related tasks. Serum anti-PLP antibody levels were highest in the insomnia group and correlated with symptom duration and demyelination severity.
Cited Product:
KAV00109, Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (Trimer) Human IgG ELISA Kit

Application in the Study:
AntibodySystem’s Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (Trimer) Human IgG ELISA Kit(CATALOG: KAV00109 was used to quantify serum anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels in long COVID patients, providing key evidence linking antibody responses to demyelination and neuropsychiatric symptoms.
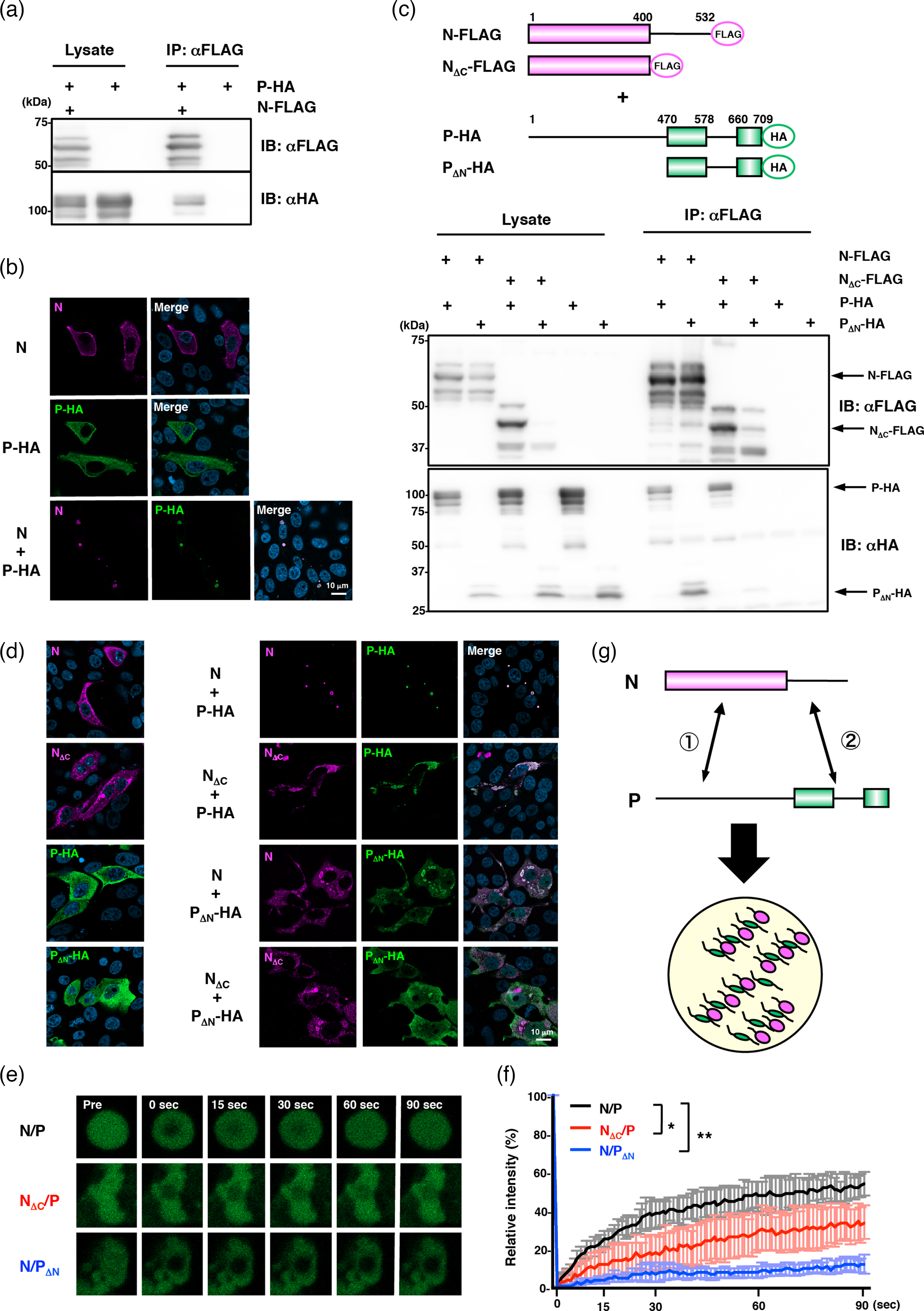
Title:
Coordinated interactions among Nipah virus N, P and M proteins drive formation of distinct inclusion bodies
DOI:
10.1099/jgv.0.002206

Key finding:
This study shows that Nipah virus forms two functionally distinct types of membraneless inclusion bodies through specific protein–protein interactions. Cytoplasmic, liquid-like inclusions depend on bipartite interactions between nucleoprotein (N) and phosphoprotein (P) and are responsible for viral RNA synthesis, whereas submembranous, low-mobility inclusions require matrix protein (M) and mediate virion assembly and budding. These findings reveal spatial compartmentalization of viral replication and assembly.
Cited Product:
PVV16601, Anti-Nipah virus/HeV Protein N/Nucleoprotein Polyclonal Antibody

Application in the Study:
AntibodySystem’s Anti-Nipah Virus/HeV Protein N Polyclonal Antibody (Cat. No. PVV16601) was used in co-immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence assays to demonstrate the critical role of bipartite N–P interactions in cytoplasmic inclusion body formation.
Title:
Reversing the Irreversible: miRNA-Targeting Mesyl Phosphoramidate Oligonucleotides Restore Sensitivity to Cisplatin and Doxorubicin of KB-8-5 Epidermoid Carcinoma Cells
DOI:
10.3390/biomedicines13123118

Key finding:
This study investigates whether mesyl phosphoramidate antisense oligonucleotides (μ-ASOs) targeting miR-17, miR-21, and miR-155 can restore chemosensitivity in multidrug-resistant human epidermoid carcinoma cells. μ-ASOs combined with chemotherapeutic agents exhibited additive to moderate synergistic effects, enabling 5–20-fold dose reductions while maintaining strong anti-tumor efficacy. Mechanistically, μ-ASOs downregulated ABCB1 and newly identified MDR-associated markers, including SEH1L, TUBA4A, and ZYX.
Cited Product:
RMN89801, Anti-SEH1L Antibody (R2T08)

Application in the Study:
AntibodySystem’s Anti-SEH1L Antibody (R2T08) (Cat. No. RMN89801) was used in Western blot analyses to demonstrate significant downregulation of SEH1L protein expression following μ-ASO treatment, providing critical protein-level evidence for the proposed mechanism underlying restored chemosensitivity.

The above are some of the scientific literatures citing AntibodySystem products in December 2025. AntibodySystem can provide a full range of scientific research reagent products, including recombinant proteins, flow cytometry antibodies, anti-IgE antibodies, phosphorylated antibodies, and ELISA kits, which accurately serve fields such as drug target research, immunoassays, allergic mechanism exploration, and tumor treatment development.
