A research team led by Professor Jianxing He from the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University published a groundbreaking study titled "Pig-to-human lung xenotransplantation into a brain-dead recipient" in Nature Medicine (IF: 50), reporting for the first time a case of genetically engineered pig lung transplantation into a brain-dead human recipient.
The three products of the AntibodySystem provided reliable data support for this study and were one of the core tools in successfully revealing the dynamic changes in humoral immunity after transplantation.

AntibodySystem Supports Front-End Scientific Research
Anti-Human IgG Antibody (R1C56) (Catalog # RHJ92831)
Anti-Human IgM Antibody (SAA0809) (Catalog # RHJ93203)
Anti-Human C4d Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # PHC45301)

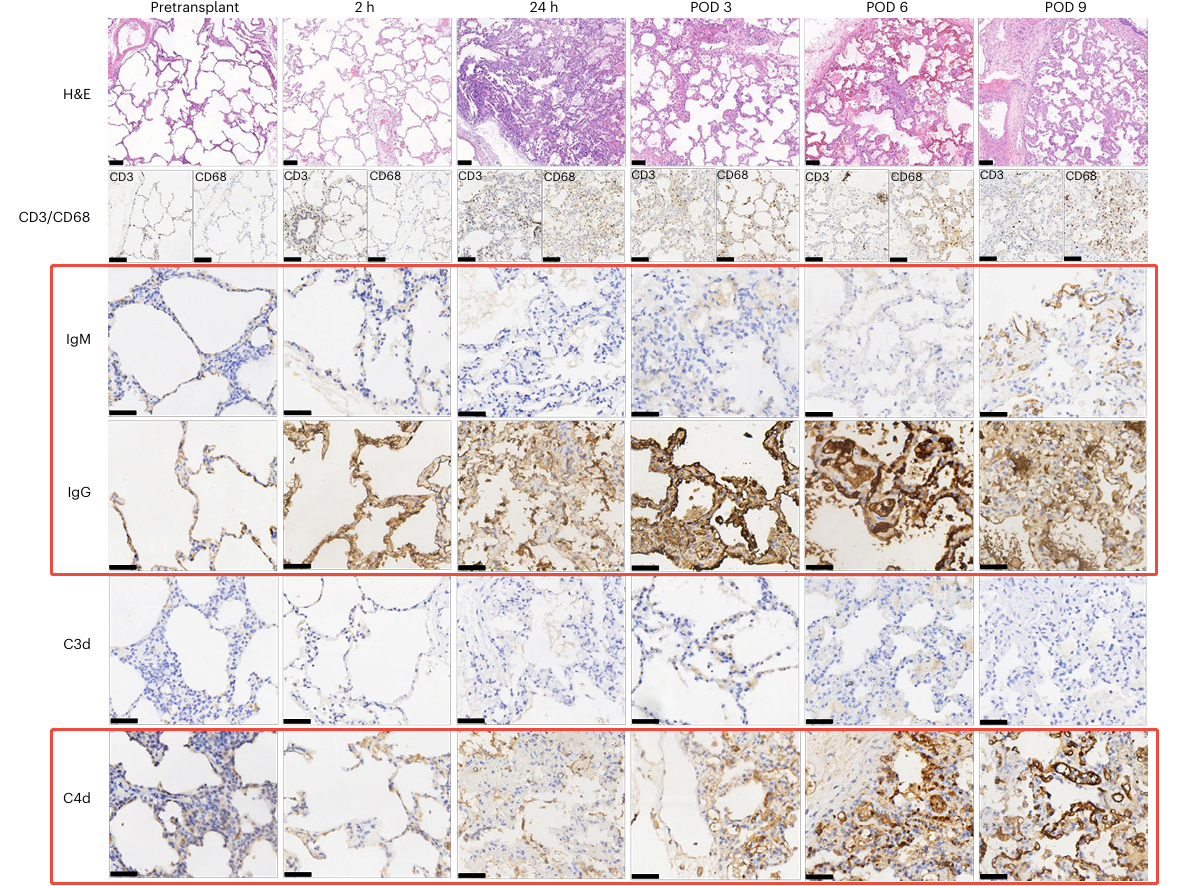
In this study, three antibodies from the AntibodySystem were utilized in immunohistochemical experiments to detect the deposition of IgG, IgM, and C4d in xenotransplanted lungs, successfully elucidating the key mechanisms of antibody-mediated rejection.
Research Contents
The study used a six-gene-edited pig as the donor. Genetic modifications included knocking out three major xenogeneic antigen genes (GGTA1, B4GALNT2, CMAH) and inserting three human protective genes (CD55, CD46, and thrombomodulin TBM), aiming to reduce hyperacute rejection and improve graft survival. The recipient was a 39-year-old brain-dead male, and the transplanted lung was closely monitored for 216 hours.
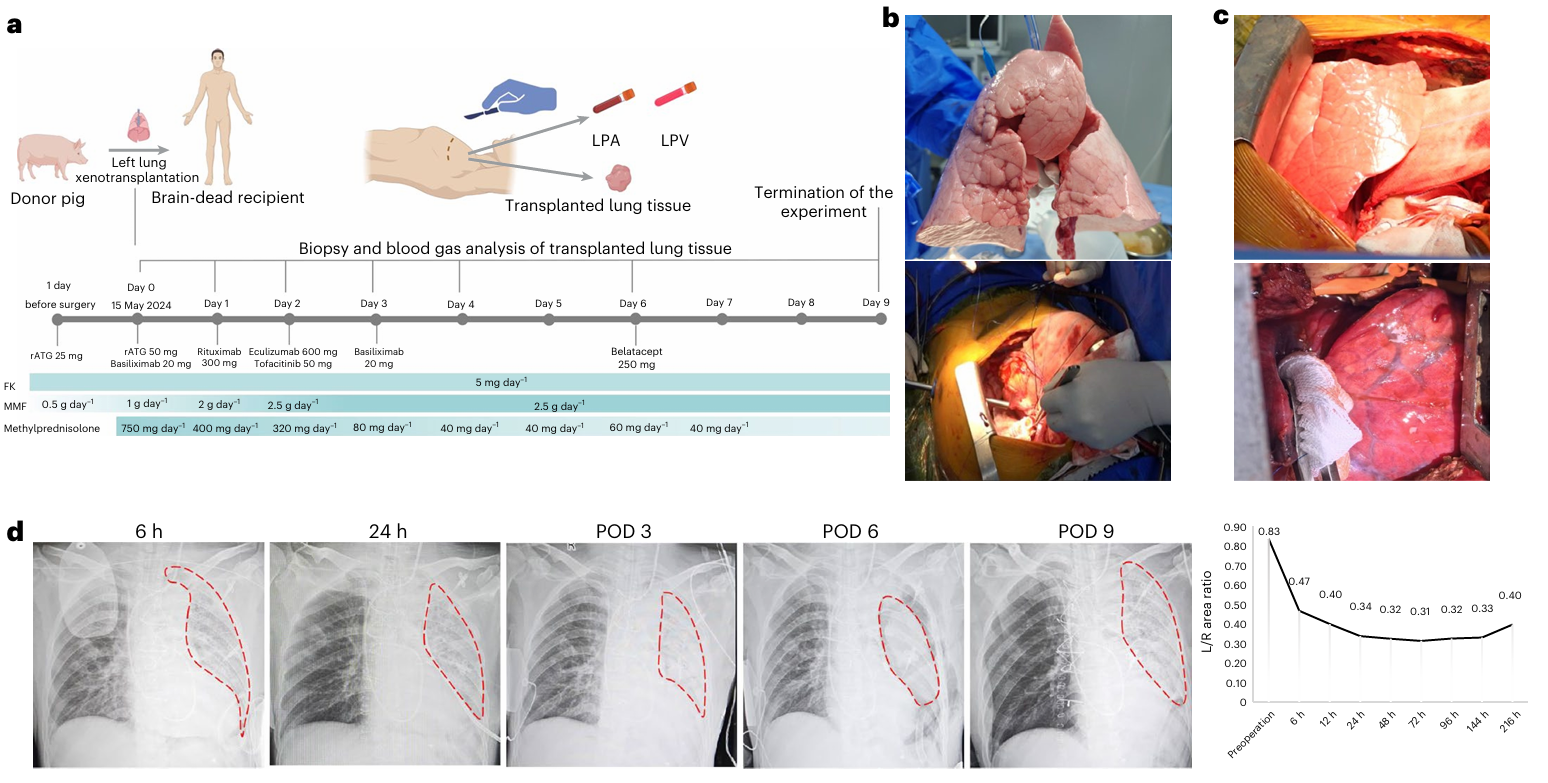
Fig. 1 Experimental outline and surgical and clinical features of the pig-to human lung xenotransplantation procedure
The results showed that the transplanted pig lung maintained basic function throughout the observation period, with no signs of hyperacute rejection or severe infection, marking a critical step toward the clinical translation of lung xenotransplantation. However, chest CT at 24 hours post-operation revealed consolidation in the dorsal region of the transplanted lung (severe pulmonary edema), consistent with primary graft dysfunction (PGD), potentially due to ischemia-reperfusion injury.
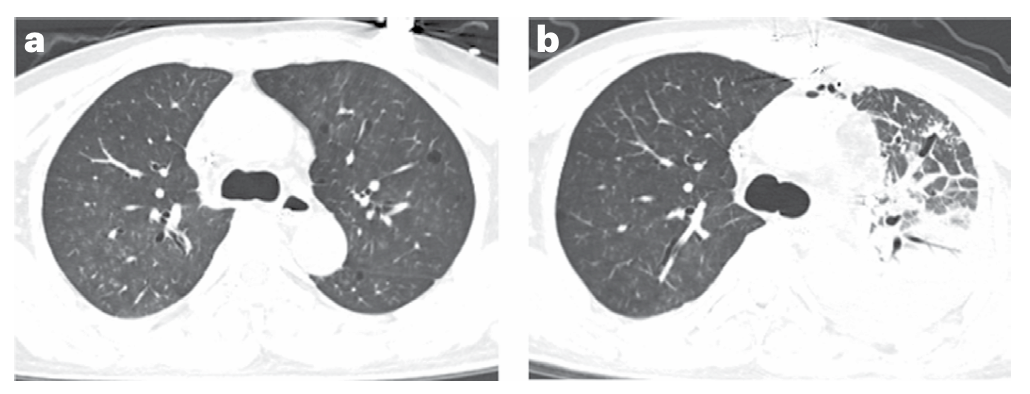
Fig. 2 Changes in lung xenograft transparency after transplantation
Additionally, antibody-mediated rejection was observed on postoperative days 3 and 6, manifested by IgG deposition along the alveolar septum accompanied by C4d complement activation. Partial recovery was noted by day 9, indicating that the immunosuppressive regimen partially controlled the humoral immune response.
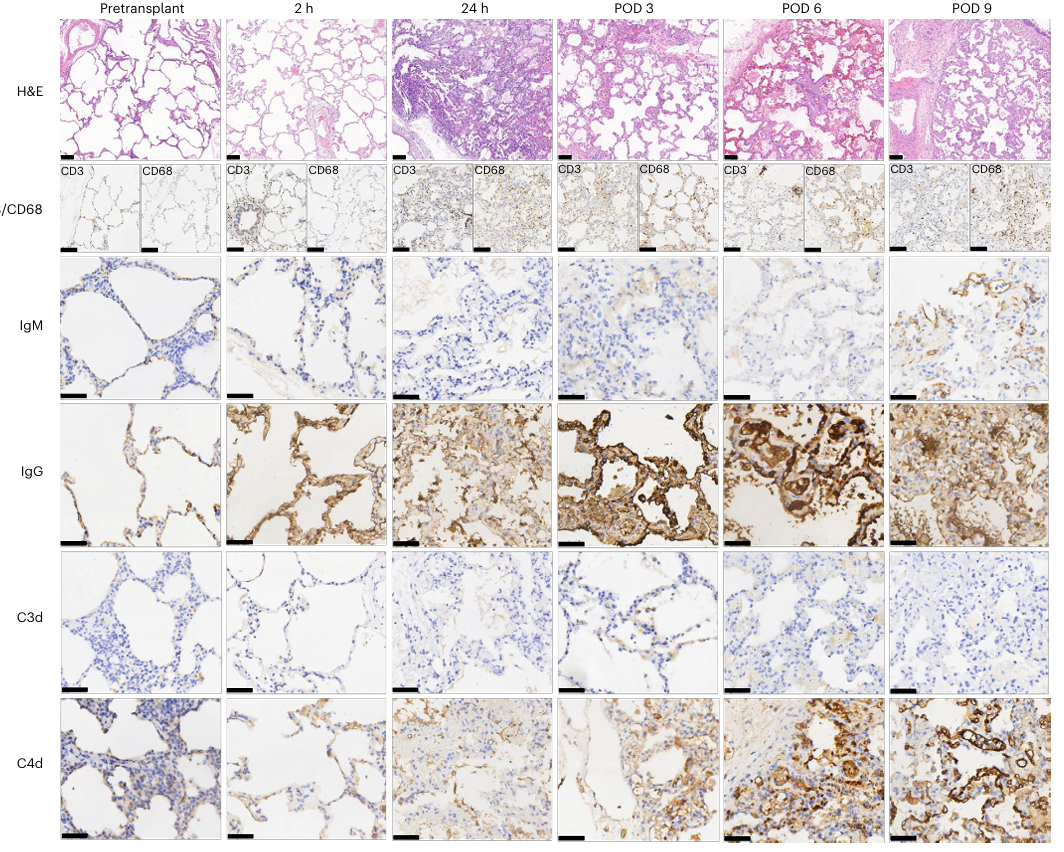
Fig. 3 Lung pathology
In terms of lung function, ventilation parameters such as lung compliance initially decreased but gradually improved, and oxygenation function declined early but recovered later.
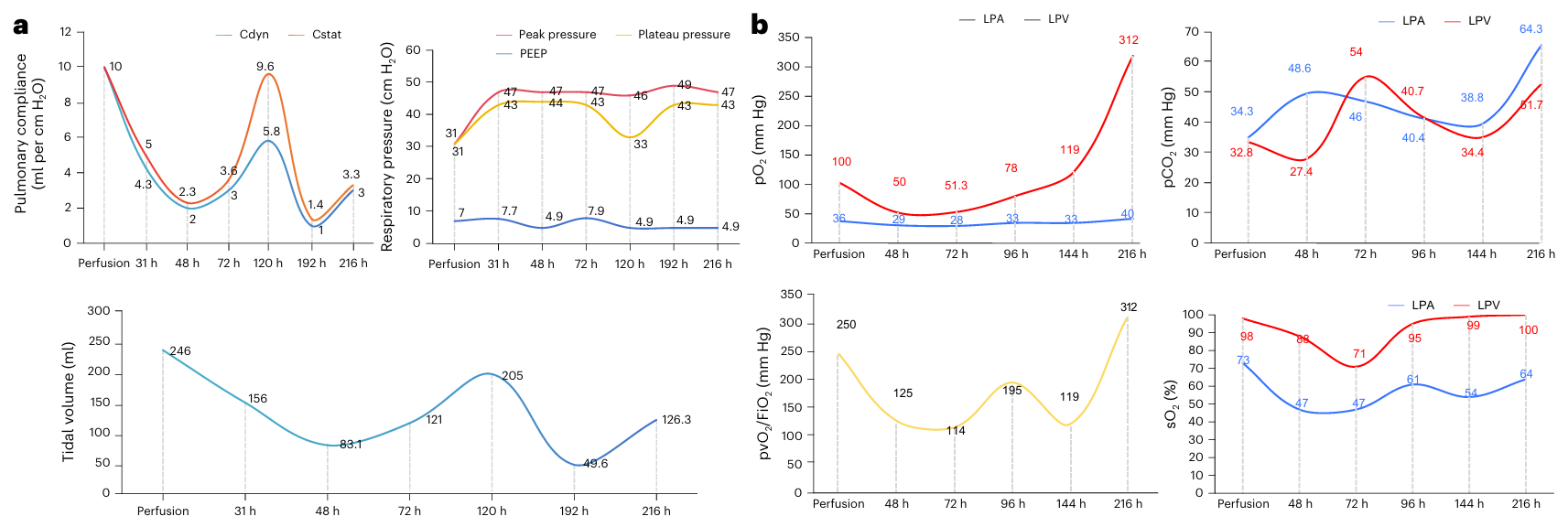
Fig. 4 Pulmonary function
The immunosuppressive strategy involved a multi-drug regimen, including anti-thymocyte globulin, basiliximab, rituximab, and eculizumab, adjusted dynamically based on immune status. Monitoring of serum antibody dynamics (Fig. 6) showed that anti-donor IgM and IgG levels decreased initially but increased again later, reflecting ongoing immune activation. Although the regimen successfully prevented hyperacute rejection, it did not fully suppress early antibody-mediated injury, suggesting a need for further optimization of immune modulation, such as introducing CD40/CD40L blockade or enhancing complement and cytokine suppression.
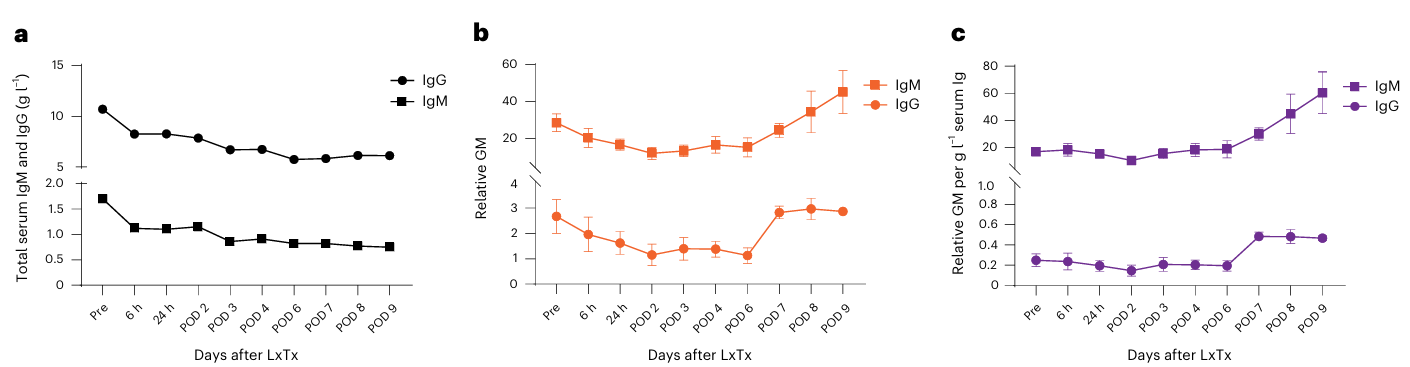
Fig. 5 Changes in serum immunoglobulin levels and serum anti-donor pig antibodies over time
The effectiveness of genetic editing was confirmed by immunohistochemistry, which showed sustained expression of CD46, CD55, and TBM in the transplanted lung, unlike in wild-type pig lungs.

Fig. 6 Immunohistochemical analysis of transgene expression in the donor lung
Regarding infection risks, metagenomic and meta-transcriptomic analyses detected no transmission of porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV-C), and other pathogen tests were negative, indicating that gene-edited pigs hold promise in terms of microbiological safety. However, given the lung’s direct interface with the environment, the risk of infection requires long-term and rigorous monitoring.
The study has several limitations. The presence of the recipient’s native right lung may have influenced immune response and functional assessment, and the lack of CD40/CD40L blockade limited the efficacy of immunosuppression. Furthermore, although the brain-death model simulates some clinical conditions, it does not fully represent the complex physiological environment of living transplantation.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates for the first time that a genetically modified pig lung can maintain functional survival in a human for up to 9 days, providing crucial evidence for the feasibility of lung xenotransplantation. However, early pulmonary edema and antibody-mediated rejection remain major challenges. Future efforts should focus on optimizing gene-editing strategies, immunosuppressive protocols, and organ preservation techniques to advance lung xenotransplantation toward clinical application. This research not only offers a new direction for addressing organ shortages but also provides valuable data for understanding the human immune response to xenogeneic organs.
The selection of AntibodySystem products for this study fully demonstrates their applicability and reliability in cutting-edge, high-standard biomedical research, highlighting its role as a critical scientific research partner. Moving forward, AntibodySystem will continue to provide robust support for global explorations at the forefront of life sciences.
|
Catalog |
Product Name |
|
RHJ92831 |
Anti-Human IgG Antibody (R1C56) |
|
RHJ93203 |
Anti-Human IgM Antibody (SAA0809) |
|
PHC45301 |
Anti-Human C4d Polyclonal Antibody |
|
DHC90705 |
Research Grade Rituximab |
|
DHB95802 |
Research Grade Basiliximab |
|
DHB90002 |
Research Grade Eculizumab |
|
DHE03402 |
Research Grade Belatacept |
|
FHC27730 |
Anti-Human CD3E Antibody (OKT3) |
|
PHE04901 |
Anti-Human CD68 Polyclonal Antibody |
|
RHD11902 |
Anti-CD46 Antibody (R3E06) |
|
FHC30912 |
Anti-Human CD55 Antibody (TS55), PE |
|
PHB96411 |
Goat Anti-Human IgG H&L Polyclonal Antibody |
