In June 2025, AntibodySystem products continued to drive global scientific advancement as research enabled by our high-specificity antibodies and recombinant proteins appeared in leading journals including Advanced Functional Materials, Cancer Research, and Chemical Engineering Journal. These publications represent breakthroughs across five critical domains: extracellular matrix regulation uncovering mechanical signaling in oral development; monkeypox virus immunoescape mechanisms; synthetic lethality approaches for targeted tumor therapy; antioxidant hydrogel-based repair of degenerative disc conditions; and nanotechnology-enhanced precision diagnostics for cardiovascular risk stratification. In each case—from fundamental mechanistic insights to advanced therapeutic and diagnostic platforms—AntibodySystem's core technologies delivered essential detection capabilities underpinning pivotal discoveries. Going forward, we remain dedicated to advancing scientific frontiers through sustained collaboration with the global research community, providing cutting-edge reagent solutions to accelerate exploration across the life sciences.
1
Impact Factor: 19
|
Title |
Photothermal Hydrogel with Mn3O4 Nanoparticles Alleviates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Scavenging ROS and Regulating Extracellular Matrix Metabolism |
|
Journal Information |
Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, e22817 |
|
Cited products |
|
|
Catalog |
Product Name |
|
Anti-dsDNA Antibody (3E10#) |
|
Annulus fibrosus (AF) injury plays a critical role in intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD). In this study, an injectable photothermal hydrogel, Mn3O4@ChS‐HA, composed of dopamine‐grafted oxidized chondroitin sulfate (dop‐OChS), adipic dihydrazide‐modified hyaluronic acid (ADH‐HA), and Mn3O4 nanoparticles is constructed to repair AF damage. In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrate that Mn3O4@ChS‐HA significantly inhibits apoptosis, delays cell senescence, reduces inflammation, and promotes autophagy, facilitating AF repair. Mn3O4@ChS‐HA, exhibits various biological functions by regulating redox homeostasis and promoting tissue repair, highlighting the potential of this approach as a promising strategy for IVDD treatment.
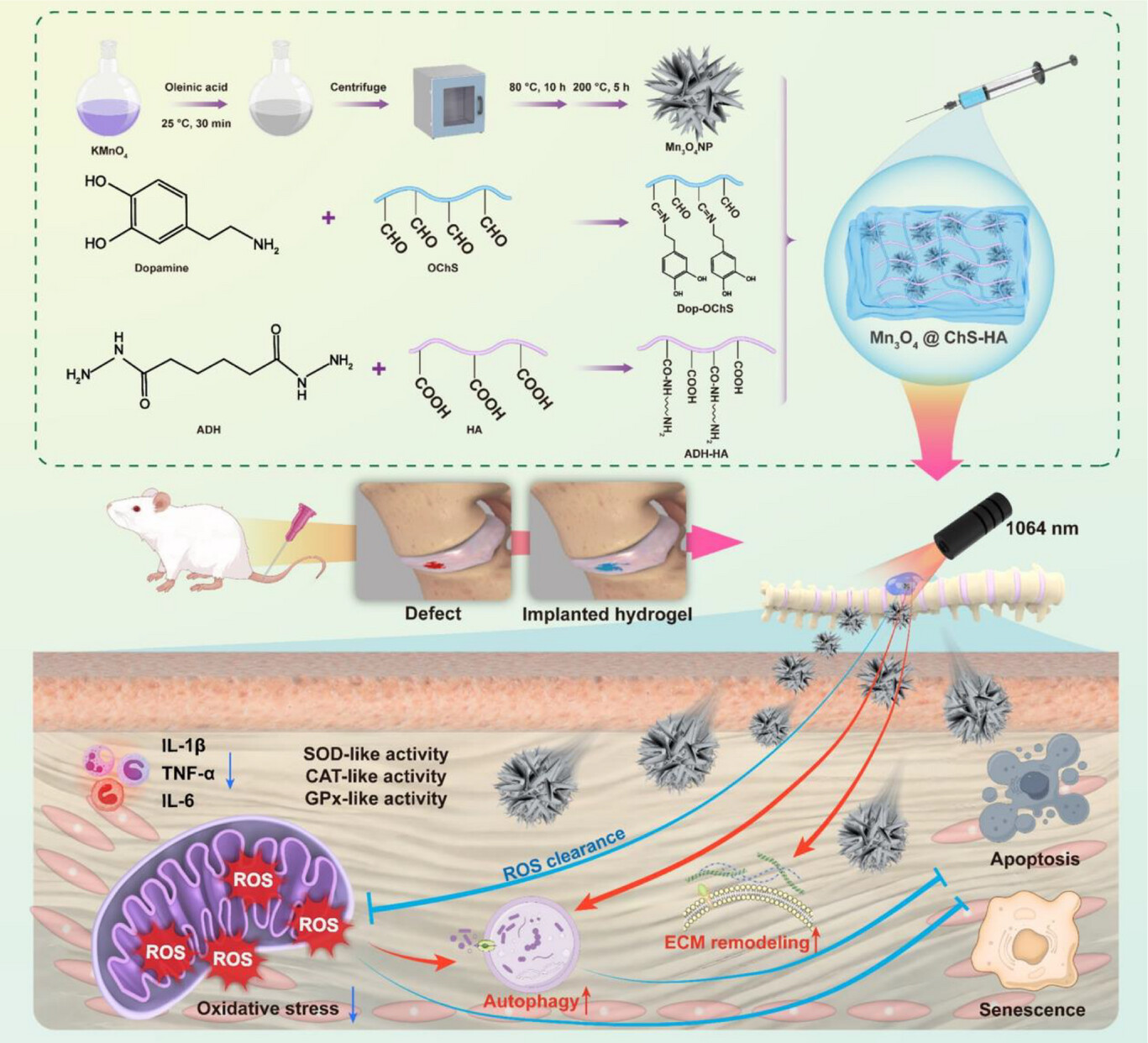
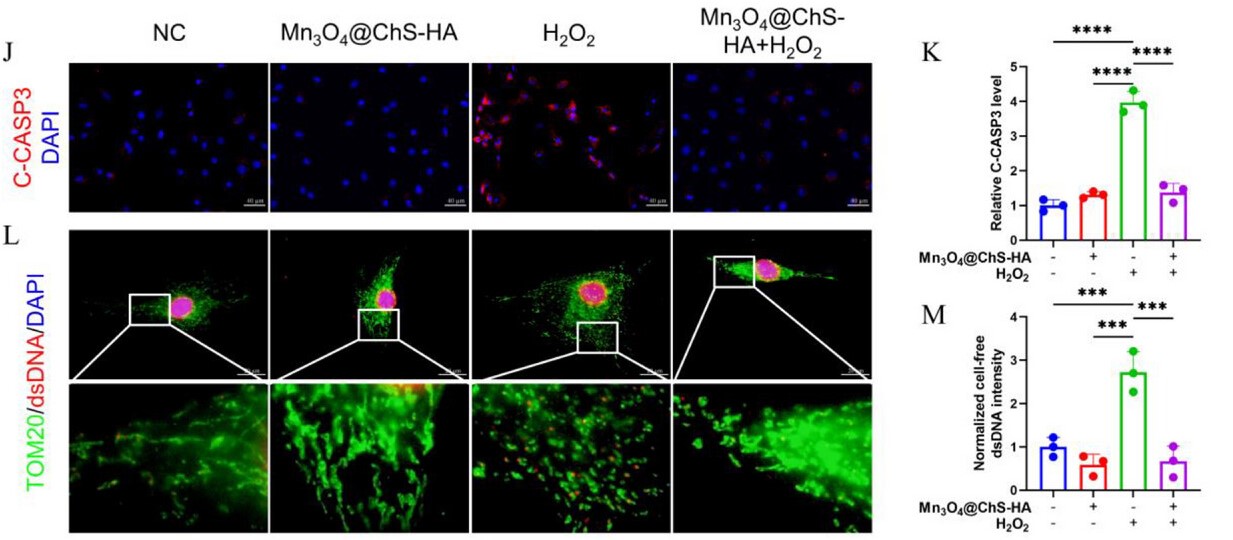
In this study, AntibodySystem’s Anti-dsDNA Antibody (3E10#) (Catalog No. RGK24020) was employed for immunofluorescence (IF) detection of oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial DNA leakage (mtDNA release into the cytosol), evaluating the protective effect of the Mn₃O₄@ChS-HA hydrogel against DNA damage. Results demonstrated that H₂O₂ stimulation significantly increased cytosolic dsDNA levels (red fluorescence), indicating mtDNA leakage and mitochondrial fission. The Mn₃O₄@ChS-HA treatment group exhibited markedly reduced cytosolic dsDNA levels, confirming its ability to maintain mitochondrial integrity.
2
Impact Factor: 16.6
|
Title |
A Genome-Wide Synthetic Lethal Screen Identifies Spermidine Synthase as a Target to Enhance Erdafitinib Efficacy in FGFR-Mutant Bladder Cancer |
|
Journal Information |
Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 16;85(12):2288-2301. |
|
Cited products |
|
|
Catalog |
Product Name |
|
Anti-Hypusine antibody (Hpu24) |
|
Mutations in the FGFR family are frequently observed in metastatic bladder cancer. Although erdafitinib, a pan-FGFR inhibitor, has shown therapeutic efficacy, resistance remains a major challenge. In this study, we performed a CRISPR-Cas9 screen and identified spermidine synthase (SRM) as a key contributor to erdafitinib resistance. SRM promotes spermidine synthesis, which catalyzes the hypusination of eIF5A, thereby enhancing the translation of HMGA2 and subsequently upregulating EGFR expression. Pharmacological inhibition of SRM significantly enhances the efficacy of erdafitinib both in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, targeting SRM may offer a promising strategy to overcome erdafitinib resistance in FGFR-mutant bladder cancer.
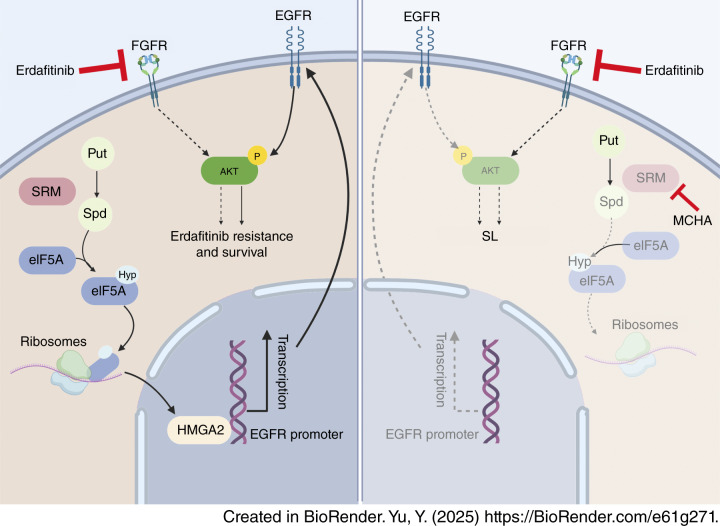
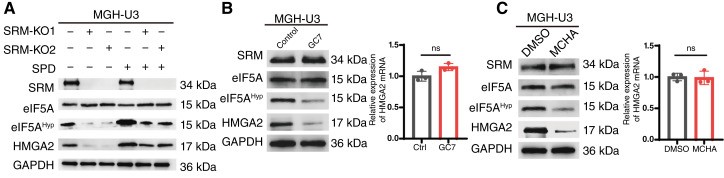
In this study, used the Anti-Hypusine antibody (Hpu24) from AntibodySystem (Catalog No. RGK08101) to detect the hypusination level of eIF5A by Western blot, in order to validate the regulatory role of SRM (spermidine synthase) in the post-translational modification of eIF5A. The results showed that in SRM-knockout bladder cancer cells, the expression level of eIF5AHyp was significantly reduced, indicating that SRM-mediated spermidine synthesis is essential for eIF5A hypusination. Treatment with the SRM inhibitor MCHA also led to a marked decrease in eIF5AHyp levels, further confirming the role of SRM. Supplementation with spermidine restored eIF5AHyp expression, demonstrating that this modification is dependent on the availability of spermidine.
3
Impact Factor: 13.2
|
Title |
LAMB3 regulates extracellular matrix stiffness and promotes odontoblast differentiation in dental papill |
|
Journal Information |
Chemical Engineering Journal, Volume 518, 2025 |
|
Cited products |
|
|
Catalog |
Product Name |
|
Recombinant Human LAMB3 Protein, N-His |
|
This study reveals that laminin subunit beta-3 (LAMB3), a key extracellular matrix (ECM) component primarily expressed by the dental epithelium, enhances collagen gel stiffness by reorganizing the homogeneity of pore size and fibril distribution, as well as increasing fibril connectivity density. These findings elucidate the role of ECM stiffness in tooth development and suggest that LAMB3-modified collagen gel could serve as a promising strategy for dentin regeneration.
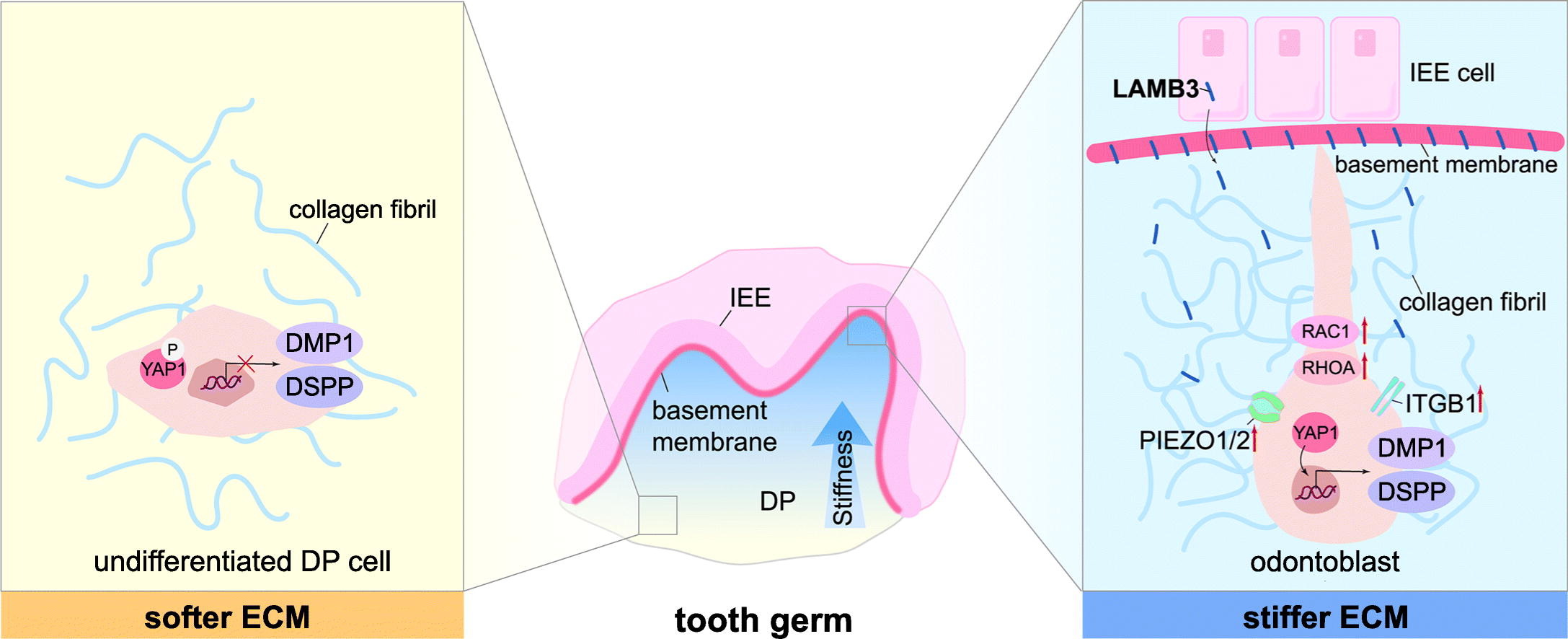
In this study, the Recombinant Human LAMB3 Protein, N-His (Catalog No. YHG64104) from AntibodySystem was used to prepare LAMB3-modified collagen gels in order to investigate the effects of LAMB3 on gel stiffness and dental papilla (DP) cell differentiation. The results demonstrated that LAMB3 significantly increased the stiffness of the collagen gel and promoted both cell polarity and odontoblast differentiation in DP cells.
4
Impact Factor: 6.7
|
Title |
Multiplex Cardiac Biomarker Profiling for Precision Coronary Artery Disease Risk Assessment Using SERS with Cubic Core–Satellite Nanostructures |
|
Journal Information |
Anal. Chem.June 28, 2025 |
|
Cited products |
|
|
Catalog |
Product Name |
|
Recombinant Human CK-MB Protein, N-His & C-Strep |
|
|
Recombinant Human TNNT2 Protein, N-His |
|
|
Anti-Human TNNT2 Polyclonal Antibody |
|
|
Anti-Human CK-MB Polyclonal Antibody |
|
In this study, the Recombinant Human LAMB3 Protein, N-His (Catalog No. YHG64104) from AntibodySystem was used to prepare LAMB3-modified collagen gels in order to investigate the effects of LAMB3 on gel stiffness and dental papilla (DP) cell differentiation. The results demonstrated that LAMB3 significantly increased the stiffness of the collagen gel and promoted both cell polarity and odontoblast differentiation in DP cells.
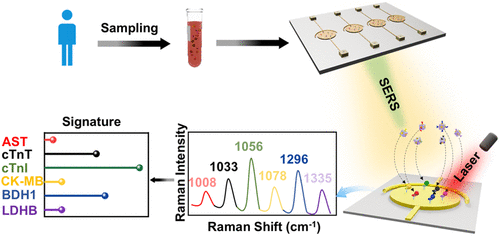
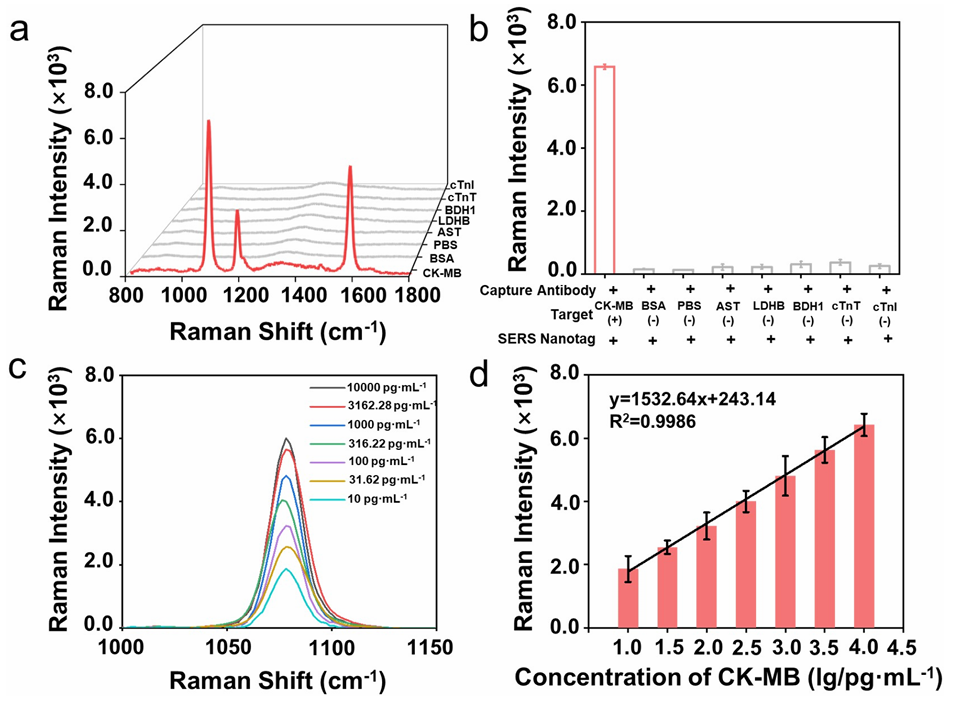
This study utilized Anti-Human TNNT2 Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog No. PHE44901), Anti-Human CK-MB Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog No. PHC21102), Recombinant Human TNNT2 Protein, N-His (Catalog No. YHE44901), and Recombinant Human CK-MB Protein, N-His & C-Strep (Catalog No. YHC21102) from AntibodySystem to construct SERS nanoprobes (barcodes) for the specific detection of cardiac biomarkers (CK-MB and cTnI) in serum. Experimental results demonstrated that the platform exhibits high specificity and sensitivity, enabling successful multiplex detection of cardiac biomarkers in clinical samples.
5
Impact Factor: 4.9
|
Title |
The conserved poxvirus membrane entry-fusion apparatus component OPG147 targets MITA/STING for immune evasion |
|
Journal Information |
PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jun 11;21(6):e1013198. |
|
Cited products |
|
|
Catalog |
Product Name |
|
Anti-Monkeypox virus/MPXV B6R/SL-159 Polyclonal Antibody |
|
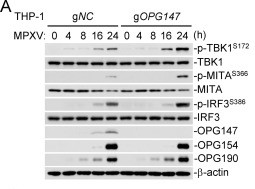
This study reveals that the monkeypox virus (MPXV) membrane fusion protein OPG147 is a conserved immune evasion factor. It suppresses the cGAS-MITA/STING-mediated innate immune response by binding to MITA/STING and blocking its ISGylation, oligomerization, and trafficking. Mutations at key OPG147 residues (F55, T116, T117) significantly enhance the host antiviral response, attenuating viral replication and pathogenicity. This work uncovers a novel mechanism by which poxviruses antagonize the MITA/STING pathway via OPG147 to achieve immune evasion.
In this study, the Anti-Monkeypox virus/MPXV B6R/SL-159 Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog No. PVV13501) from AntibodySystem was employed for Western blot analysis. This antibody was used to detect the expression level of the viral early protein OPG190 post-MPXV infection, thereby validating successful viral infection and gene expression. The experimental results demonstrated that OPG190 expression increased progressively after infection, confirming successful viral infection and early protein expression.
The studies highlighted above represent select June 2025 publications citing AntibodySystem research tools. Complementing these citations, our portfolio delivers comprehensive solutions spanning recombinant proteins, flow cytometry antibodies, anti-IgE antibodies, phospho-specific antibodies, and ELISA kits. These precision reagents support critical scientific workflows across drug target identification/validation, immune system profiling, mechanistic studies of allergic disorders, and oncology therapeutic development.
