Japanese encephalitis (JE), caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), is a severe mosquito-borne disease endemic to Asia. Current studies widely recognize pigs and birds as the primary "amplifying hosts" of JEV, where mosquitoes transmit the virus to humans after feeding on infected animals, perpetuating the natural transmission cycle. However, the role of other mammals, such as sheep, in JEV transmission has long been unclear. In recent years, suspected JEV infections with neurological symptoms have been sporadically reported in sheep flocks in China, but direct evidence was lacking.
A research team from the Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, revealed that sheep may act as potential amplifying hosts, forming a new transmission cycle in rural areas without pig farming. Their findings, published in Science Advances under the title Sheep serve as amplifying hosts of Japanese encephalitis virus, increasing the risk of human infection, mark the first isolation of a JEV strain from sheep and experimentally demonstrate the critical role of sheep in JEV transmission.

Highlight
Global First: Isolation of JEV strain from sheep, confirming sheep as natural hosts.
Key Data: Peak viremia in sheep reached 10⁴ TCID50/ml, with mosquito infection rates exceeding 40%, comparable to pigs.
Practical Implications: Redefines JEV control strategies, necessitating inclusion of sheep in surveillance systems to disrupt the "sheep-mosquito-human" transmission chain.
Isolation of JEV Strain from Sheep with Neurological Symptoms
In 2022, a disease outbreak occurred in a Shanghai, China sheep farm, affecting 11 lambs exhibiting neurological signs such as circling and ataxia. Histopathological analysis of brain tissue revealed lymphohistiocytic perivascular cuffing (indicated by arrows), and RT-qPCR confirmed JEV as the sole pathogen, excluding other agents like Brucella or pseudorabies virus. Inoculation of brain homogenates into BHK-21 cells led to the isolation of the JEV strain SH2201, which replicated efficiently, peaking at 1.4×10⁶ TCID50/ml at 48 hours post-infection.
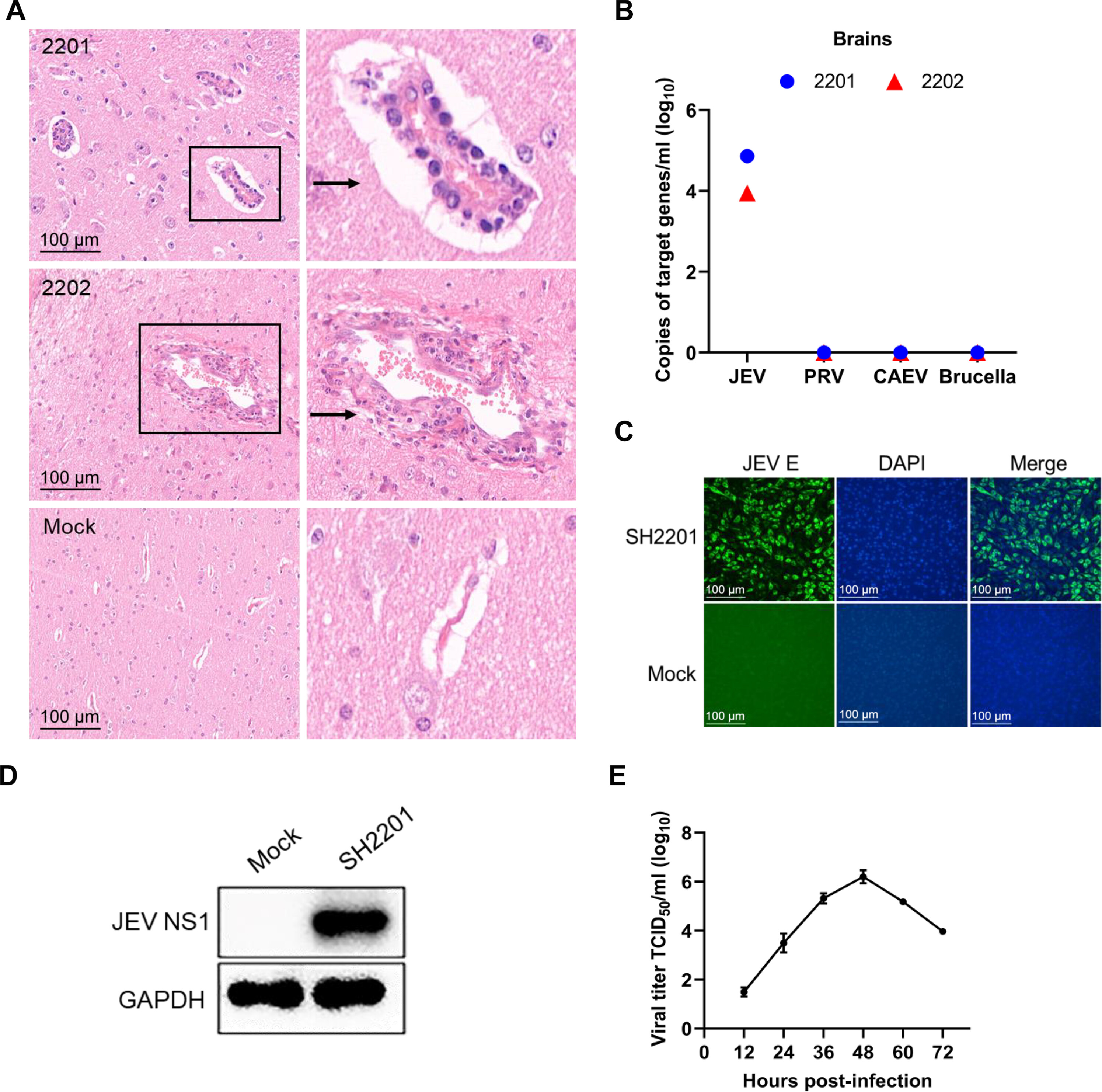
Fig. 1. Isolation of JEV from sheep
Genetic Characterization and High Virulence of SH2201
Whole-genome sequencing classified SH2201 as genotype I (GI), sharing 99.8% nucleotide identity with the pig-derived SD12 strain from China. Critical virulence-associated residues in the E protein (e.g., E107, E138, E176) matched those of known virulent JEV strains.
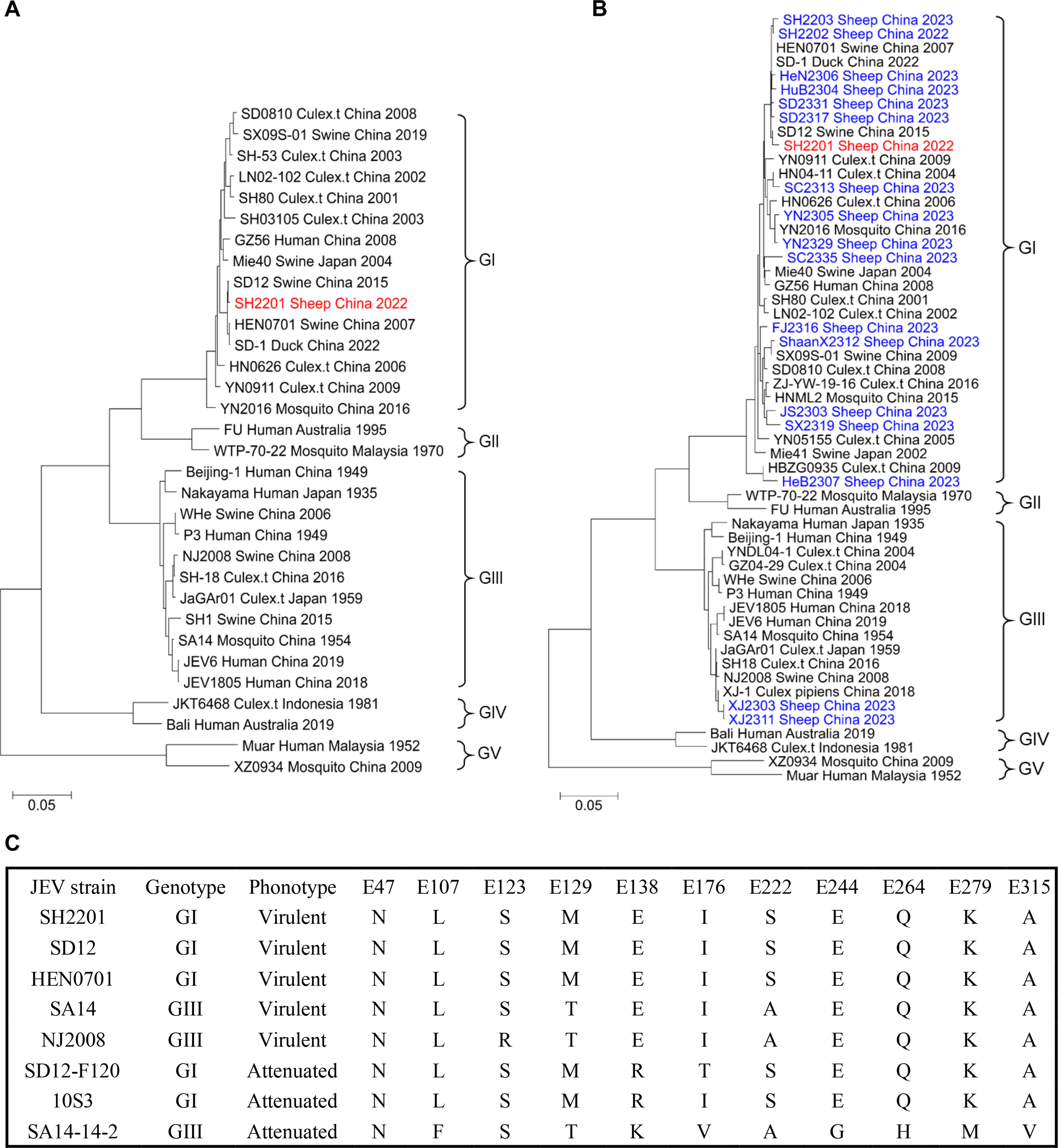
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic analysis of JEV strains
In mice, intracerebral inoculation of SH2201 at the lowest dose (10⁰ PFU) caused 25% mortality, while intraperitoneal LD₅₀ was 10¹.³⁵ PFU, comparable to virulent reference strains. Histopathology showed encephalitis lesions, including perivascular inflammation and meningitis.
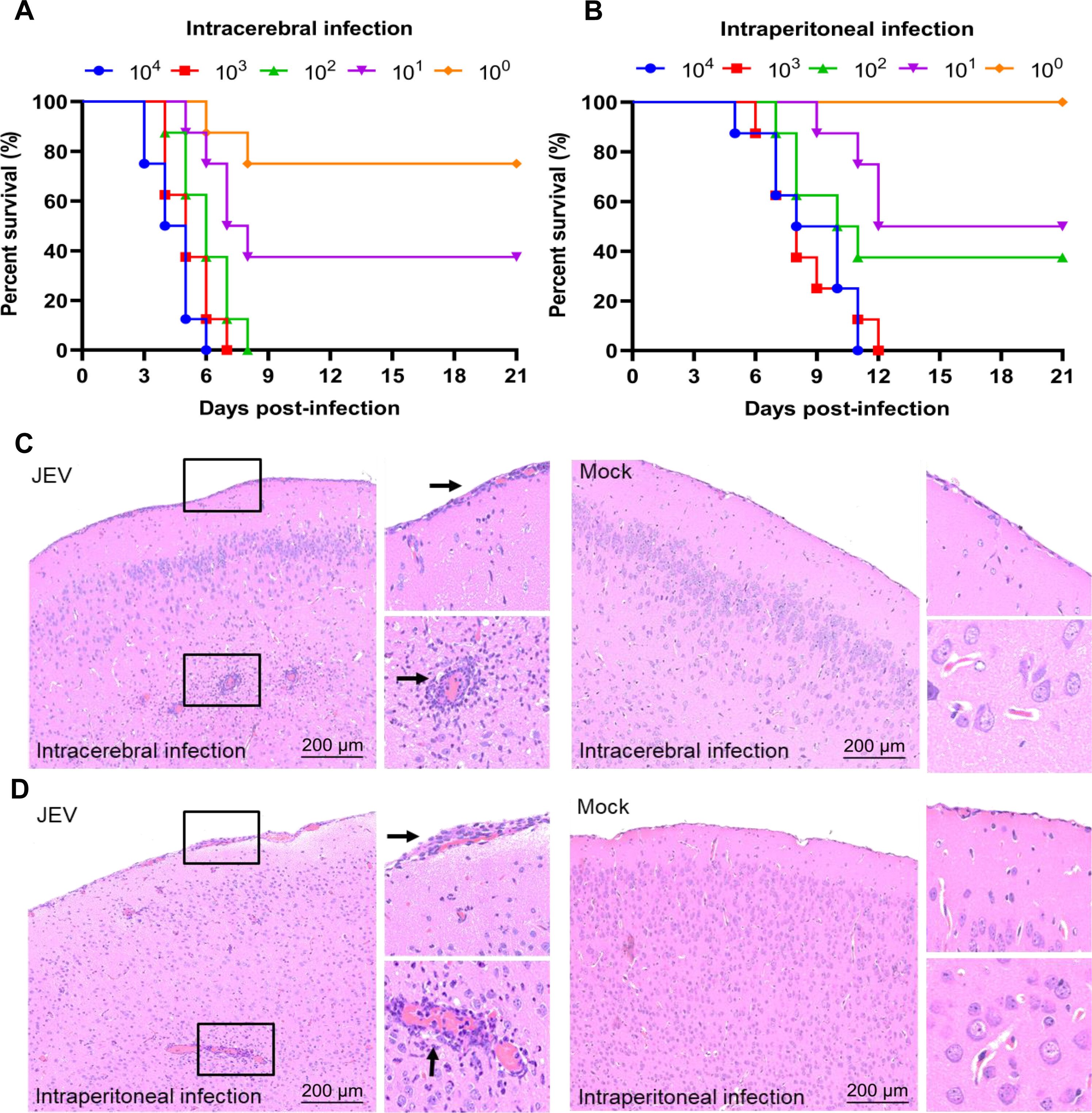
Fig. 3. Virulence of the SH2201 strain in mice
Viremia and Viral Shedding in Infected Sheep
Subcutaneous or intravenous infection of 50-day-old Hu sheep with 10⁶ PFU of SH2201 induced viremia peaking at 3.2×10⁴ TCID50/ml (subcutaneous) and 4.2×10⁴ TCID50/ml (intravenous), persisting for 3–6 days. Viral RNA was detected in nasal (1.1×10⁴ RNA copies/ml) and anal swabs (3.8×10³ RNA copies/ml), with sustained shedding for 6–11 days. High viral loads were also observed in tonsils (3.2×10³ TCID50/ml), mirroring JEV persistence in pigs.
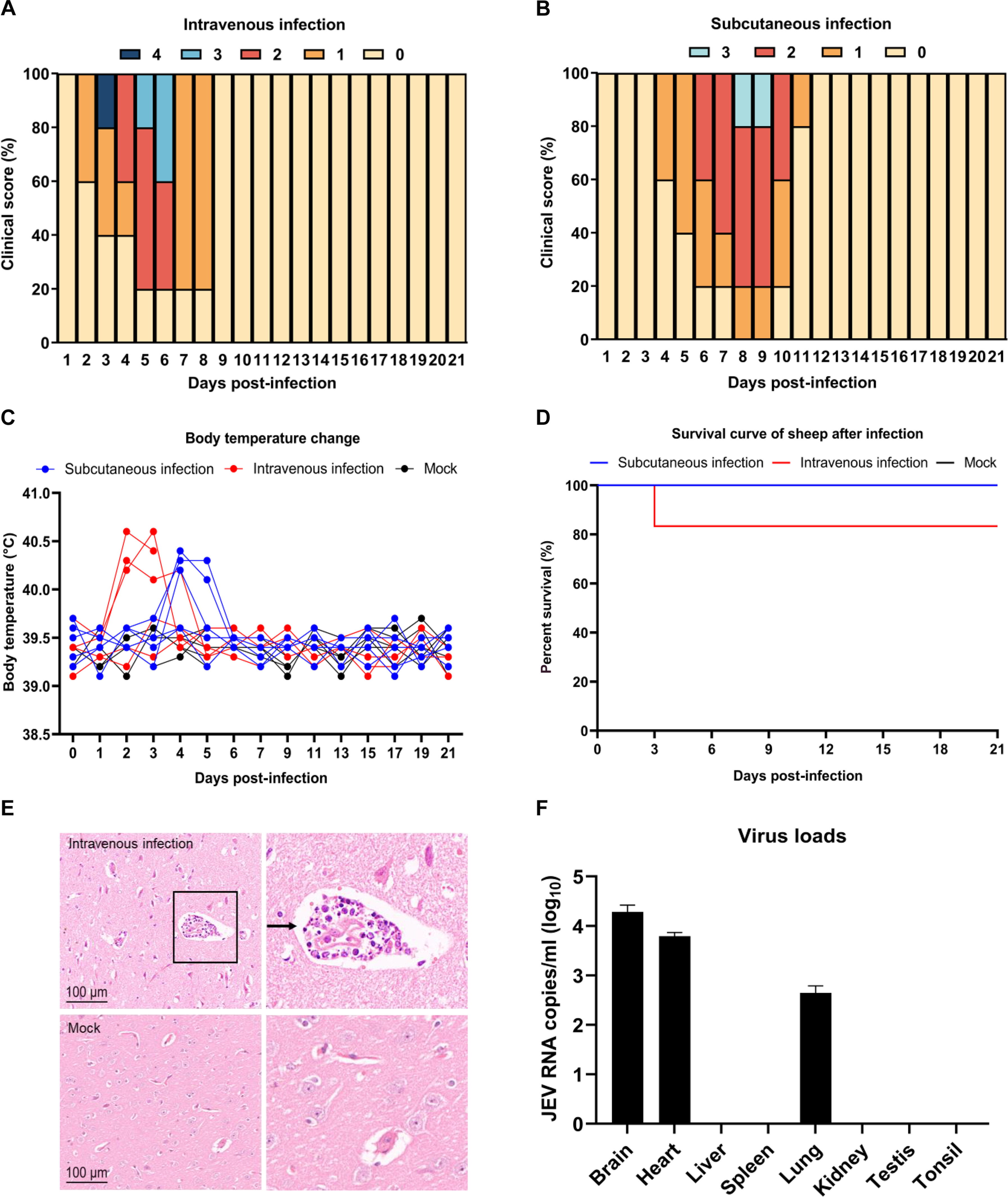
Fig. 4. Pathogenicity of the SH2201 strain in sheep
In the brain tissue of infected sheep, high virus concentrations (2.0×10⁴ RNA copies/ml) were detected. Moreover, pathological sections exhibited typical encephalitis lesions that were comparable to those observed in human patients.
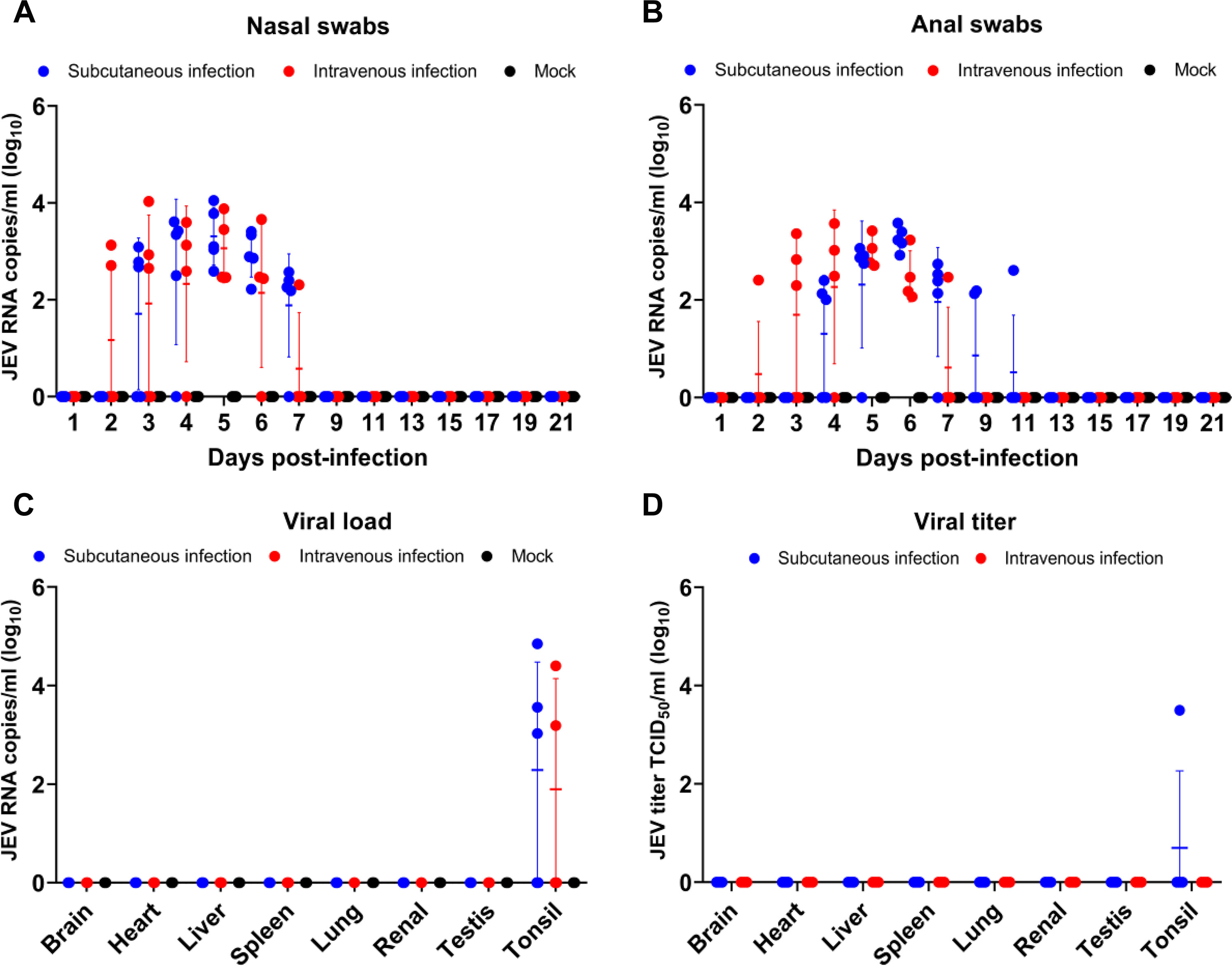
Fig. 5. Detection of viral shedding in JEV-infected sheep
Mosquito Transmission Experiments
Culex pipiens pallens, Cx. pipiens quinquefasciatus, and Aedes albopictus fed on viremic sheep blood exhibited infection rates of 48.6%, 57.1%, and 40.6% at 14 days post-infection (dpi), respectively. Viral dissemination to salivary glands was confirmed in 39.3%–60% of mosquitoes, demonstrating efficient JEV transmission potential.
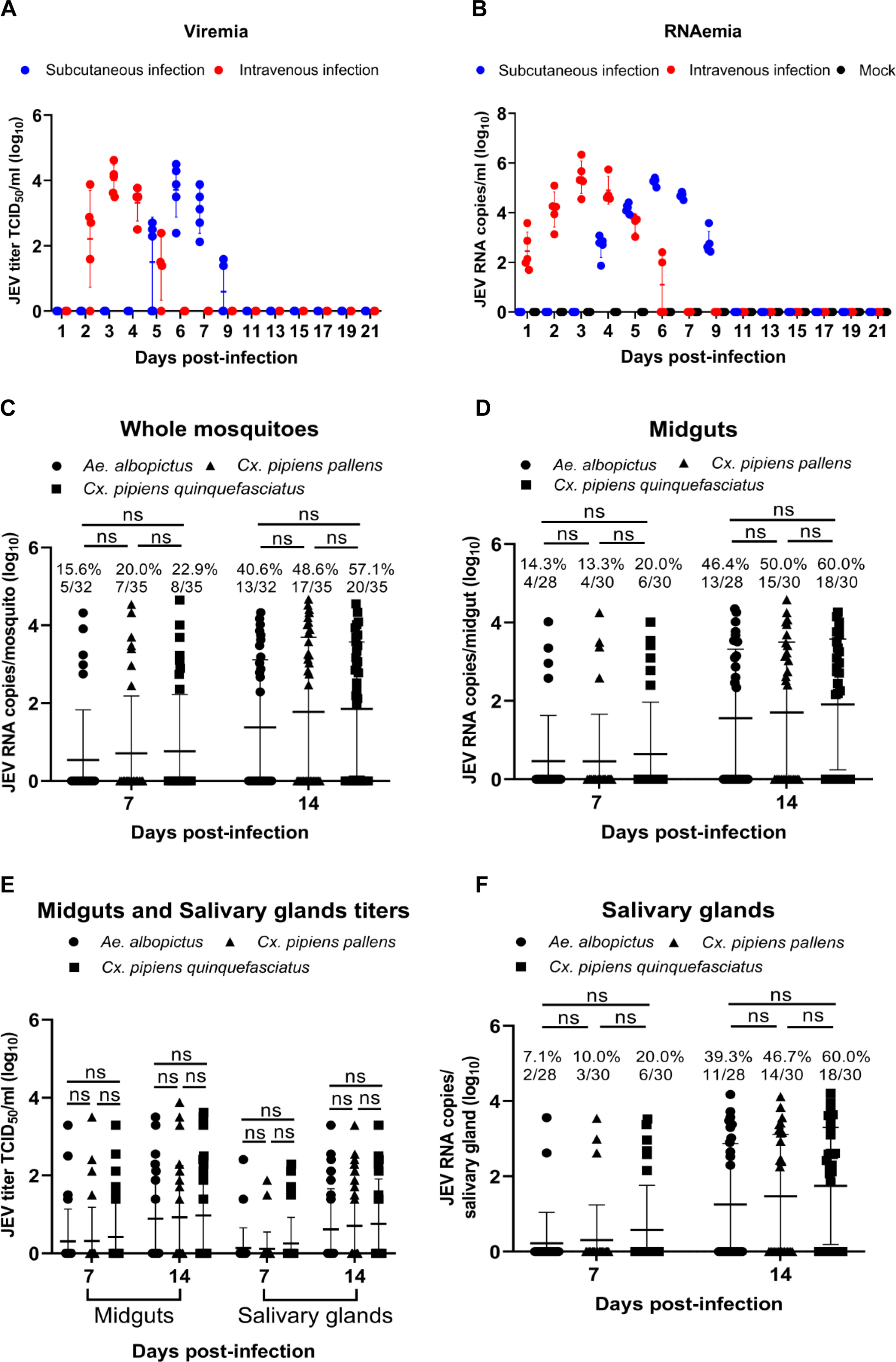
Fig. 6. Viremia levels in sheep infected with the SH2201 strain
Epidemiological Survey of JEV in Chinese Sheep
Among 3,349 serum samples from 31 provinces in China, 19 provinces showed JEV RNA positivity (0.7%–4.6%), and 20 provinces had seropositivity rates of 2.0%–26.7%. In Xinjiang—a region without pig farming—JEV strains from sheep were phylogenetically related to local mosquito-derived strains, confirming cross-species transmission.
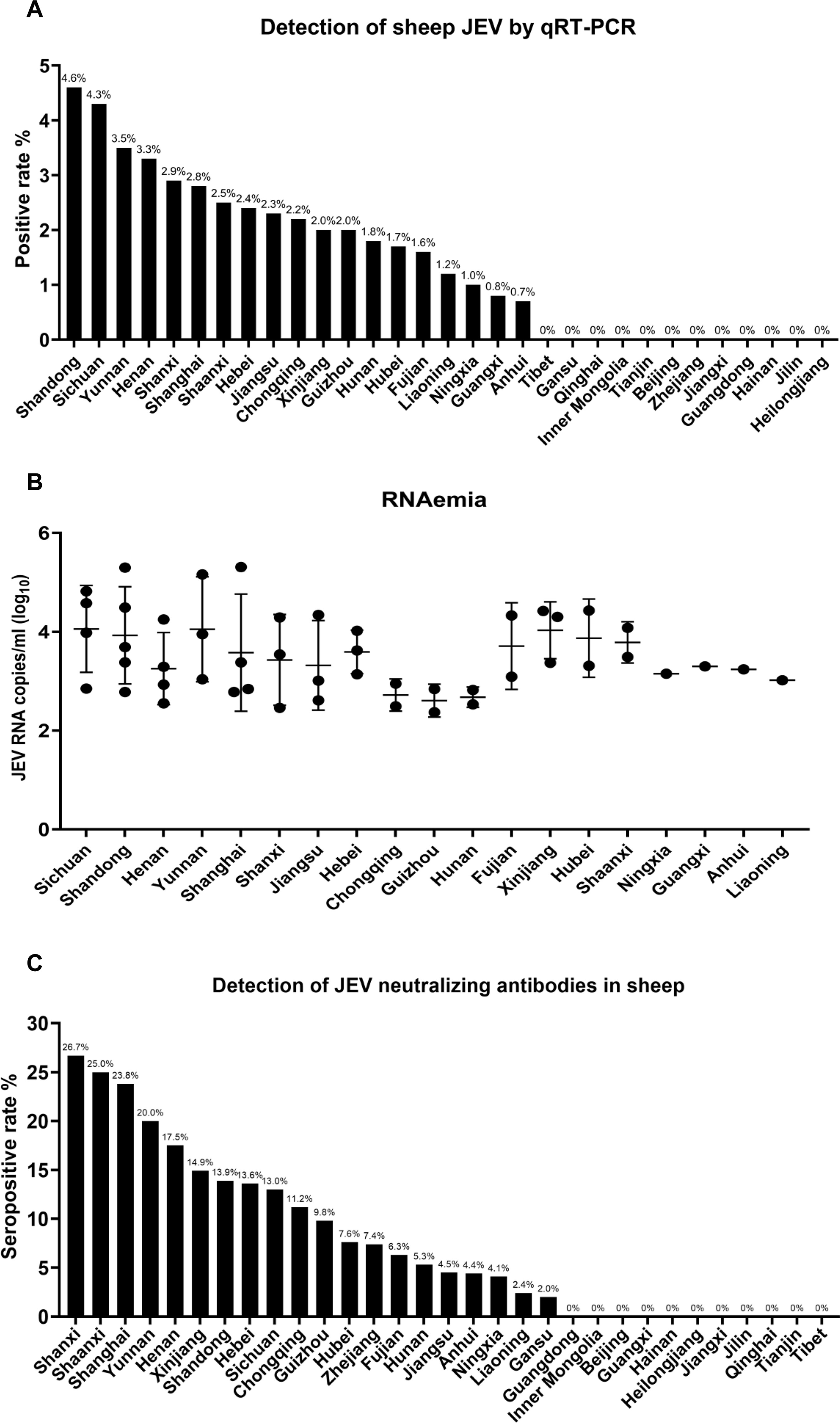
Fig. 7. Prevalence of JEV in field sheep
Conclusions
Sheep as Novel Amplifying Hosts: Sheep develop viremia levels equivalent to pigs, enabling mosquito-mediated transmission and potentially sustaining independent transmission cycles in pig-free regions.
Elevated Public Health Risk: Traditional control strategies focused on pigs and birds must expand to include sheep, particularly in pastoral areas (e.g., Northwest China, Mongolian grasslands).
Threat to Livestock Health: JEV infection may cause neurological symptoms or death in sheep, necessitating improved diagnostics and economic loss prevention.
This study redefines the JEV transmission model, urging updated surveillance protocols, sheep-targeted vaccines, and enhanced mosquito control. For the public, mosquito avoidance and vaccination remain critical for JE prevention.
JEV related product list:
Recombinant Protein
|
Catalog No. |
Product name |
|
YVV25701 |
Recombinant JEV Envelope protein E Protein, N-TrxA-His & C-His |
|
YVV25702 |
Recombinant JEV Envelope protein E Protein, N-His |
|
YVV25801 |
Recombinant JEV NS1/Non-structural protein 1 Protein, N-TrxA-His & C-His |
|
YVV39801 |
Recombinant JEV NS3/Serine protease NS3 Protein, N-His |
|
EVV25801 |
Recombinant JEV NS1/Non-structural protein 1 Protein, C-Fc |
|
EVV25802 |
Recombinant JEV NS1/Non-structural protein 1 Protein, C-His |
|
YVV25802 |
Recombinant JEV NS1/Non-structural protein 1 Protein, N-His |
|
YVV43201 |
Recombinant JEV NS5 Protein, N-His |
|
YVV25704 |
Recombinant JEV Envelope protein E Protein, N-His |
|
YVV43301 |
Recombinant JEV Capsid protein C/Core protein Protein, N-GST & C-His |
|
YVV43402 |
Recombinant JEV Peptide pr Protein, N-GST & C-His |
Antibody
|
Catalog No. |
Product name |
|
PVV25801 |
Anti-JEV NS1/Non-structural protein 1 Polyclonal Antibody |
|
PVV39801 |
Anti-JEV NS3/Serine protease NS3 Polyclonal Antibody |
|
PVV25701 |
Anti-JEV Envelope protein E Polyclonal Antibody |
|
PVV25702 |
Anti-JEV Envelope protein E Polyclonal Antibody |
|
PVV43201 |
Anti-JEV NS5 Polyclonal Antibody |
|
PVV43301 |
Anti-JEV Capsid protein C/Core protein Polyclonal Antibody |
|
PVV43401 |
Anti-JEV Peptide pr Polyclonal Antibody |
|
RVV25701 |
Anti-JEV Envelope protein E Antibody (12B02) |
|
RVV25702 |
Anti-JEV Envelope protein E Antibody (2H4) |
